
Building a Simple CRUD Application with Express and MongoDB
Building a Simple CRUD Application with Express and MongoDB 관련


For a long time, I didn’t dare venture into back end development. I felt intimidated because of my lack of an academic background in programming.
I remember when I eventually built up the courage to try back end development. I had such a hard time understanding the documentation for Express, MongoDB, and Node.js that I gave up.
I eventually went back and worked through my confusion. Now, one year later, I understood how to work with these tools. So, I decided to write this comprehensive tutorial so you won’t have to go through the same headache that I went through.
CRUD, Express and MongoDB
CRUD, Express and MongoDB are big words for a person who has never touched any server-side programming in their life. Let’s quickly introduce what they are before we diving into the tutorial.
Express is a framework for building web applications on top of Node.js. It simplifies the server creation process that is already available in Node. In case you were wondering, Node allows you to use JavaScript as your server-side language.
MongoDB is a database. This is the place where you store information for your web websites (or applications).
CRUD is an acronym for Create, Read, Update and Delete. It is a set of operations we get servers to execute (POST, GET, PUT and DELETE respectively). This is what each operation does:
- Create (POST): Make something
- Read (GET): Get something
- Update (PUT): Change something
- Delete (DELETE): Remove something
If we put CRUD, Express and MongoDB together into a single diagram.
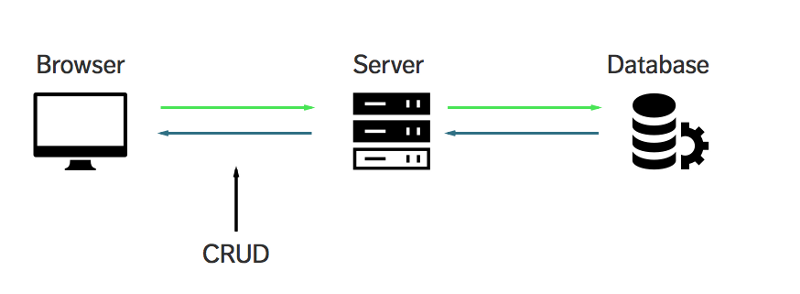
Does CRUD, Express and MongoDB makes more sense to you now?
Great. Let’s move on.
What we’re building
We’re going to build an application simple list application that allows you to keep track of things within a list (like a Todo List for example).
Well, a todo list is kind of boring. How about we make a list of quotes from Star wars characters instead? Awesome, isn’t it? Feel free to take a quick look at the demo before continuing with the tutorial. Also, this is where (zellwk/crud-express-mongo) you can find the finished code for the application.
By the way, what we’re building isn’t a sexy single page app. We’re mainly focusing on how to use CRUD, Express and Mongo DB in this tutorial, so, more server-side stuff. I’m not going to emphasize style.
You’ll need two things to get started with this tutorial:
- You shouldn’t be afraid of typing commands into a shell. Check out this article if you currently are.
- You need to have Node installed.
To check if you have Node installed, open up your command line and run the following code:
node -v
You should get a version number if you have Node installed. If you don’t, you can install Node either by downloading the installer from Node’s website or downloading it through package managers like Homebrew (Mac) and Chocolatey (Windows).
Getting started
Start by creating a folder for this project. Feel free to call it anything you want. Once you navigate into it, run the npm init command.
This command creates a package.json file which helps you manage dependencies that we install later in the tutorial.
npm init
Just hit enter through everything that appears. I’ll talk about the ones you need to know as we go along.
Running Node for the first time in your life
The simplest way to use node is to run the node command, and specify a path to a file. Let’s create a file called server.js to run node with.
touch server.js
When the execute the server.js file, we want to make sure it’s running properly. To do so, simply write a console.log statement in server.js:
console.log('May Node be with you')

server.js in your command line and you should see the statement you loggedGreat. Let’s move on and learn how to use Express now.
Using Express
We first have to install Express before we can use it in our application. Installing Express is pretty easy. All we have to do is run an install command with Node package manager (npm), which comes bundled with Node.
Run the npm install express -- save command in your command line:
npm install express --save
package.jsonNext, we use express in server.js by requiring it.
const express = require('express');const app = express();
The first thing we want to do is to create a server where browsers can connect to. We can do so with the help of a listen method provided by Express:
app.listen(3000, function() { console.log('listening on 3000')})
Now, run node server.js and navigate to localhost:3000 on your browser.
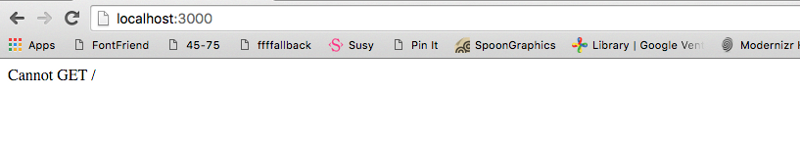
That’s a good sign. It means we can now communicate to our express server through the browser. This is where we begin CRUD operations.
CRUD — READ
The READ operation is performed by browsers whenever you visit a webpage. Under the hood, browsers sends a GET request to the server to perform a READ operation. The reason we see the “cannot get /” error is because we have yet to send anything back to the browser from our server.
In Express, we handle a GET request with the get method:
app.get(path, callback)
The first argument, path, is the path of the GET request. It’s anything that comes after your domain name.
When we’re visiting localhost:3000, our browsers are actually looking for localhost:3000/. The path argument in this case is /.
The second argument is a callback function that tells the server what to do when the path is matched. It takes in two arguments, a request object and a response object:
app.get('/', function (request, response) { // do something here})
For now, let’s write “Hello World” back to the browser. We do so by using a send method that comes with the response object:
app.get('/', function(req, res) { res.send('Hello World')})// Note: request and response are usually written as req and res respectively.
I’m going to start writing in ES6 code and show you how to convert to ES6 along the way as well. First off, I’m replacing the function() with the ES6 arrow function. The below code is the same as the above code:
app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('hello world')})
Now, restart your server by doing the following:
- Stop the current server by hitting Ctrl+C in the command line.
- Run node
server.jsagain.
Then, navigate to localhost:3000 on your browser.
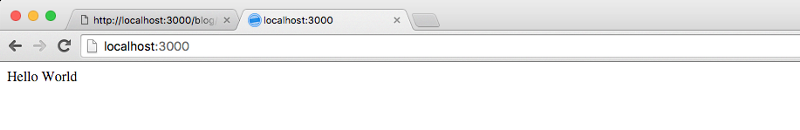
Great. Let’s change our app so we serve an index.html page back to the browser instead. To do so, we use the sendFile method that’s provided by the res object.
app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.sendFile(__dirname + '/index.html') // Note: __dirname is the path to your current working directory. Try logging it and see what you get! // Mine was '/Users/zellwk/Projects/demo-repos/crud-express-mongo' for this app.})
In the sendFile method above, we told Express to serve an index.html file that can be found in the root of your project folder. We don’t have that file yet. Let’s make it now.
touch index.html
Let’s put some text in our index.html file as well:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>MY APP</title>
</head>
<body>May Node and Express be with you.</body>
</html>
Restart your server and refresh your browser.
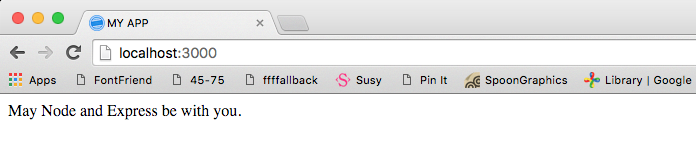
This is how Express handles a GET request (READ operation) in a nutshell.
At this point, you probably have realized that you need to restart your server whenever you make a change to server.js. This is process is incredibly tedious, so let’s take a quick detour and streamline it by using a package called nodemon.
Enter Nodemon
Nodemon restarts the server automatically whenever you save a file that the server uses. We can install Nodemon by using the following command:
npm install nodemon --save-dev
Note
The reason we’re using a --save-dev flag here is because we’re only using Nodemon when we’re developing. This flag would save Nodemon as a devDependency in your package.json file.
Moving on, Nodemon behaves exactly the same as node, which means we can run our server by calling nodemon server.js. However, we can’t do it in the command line right now because Nodemon isn’t installed with a -g flag.
There’s one other way to run Nodemon — we can execute Nodemon from the node_modules folder. The code looks like this:
./node_modules/.bin/nodemon server.js
That’s a handful to type. One way to make it simpler is to create a script key in package.json.
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon server.js"
}
// ...
}
Now, you can run npm run dev to trigger nodemon server.js.
Back to the main topic. We’re going to cover the CREATE operation next.
CRUD — CREATE
The CREATE operation is performed only by the browser if a POST request is sent to the server. This POST request can triggered either with JavaScript or through a
element.
Let’s find out how to use a
element to create new entries for our star wars quote app for this part of the tutorial.
To do so, you first have to create a
element and add it to your index.html file. You need to have three things on this form element:
- An action attribute
- a method attribute
- and name attributes on all elements within the form
<form action="/quotes" method="POST">
<input type="text" placeholder="name" name="name">
<input type="text" placeholder="quote" name="quote">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
The action attribute tells the browser where to navigate to in our Express app. In this case, we’re navigating to /quotes. The method attribute tells the browser what to request to send. In this case, it’s a POST request.
On our server, we can handle this POST request with a post method that Express provides. It takes the same arguments as the GET method:
app.post('/quotes', (req, res) => { console.log('Hellooooooooooooooooo!')})
Restart your server (hopefully you’ve set up Nodemon so it restarts automatically) and refresh your browser. Then, enter something into your form element.
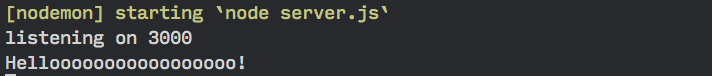
Great, we know that Express is handling the form for us right now. The next question is, how do we get the input values with Express?
Turns out, Express doesn’t handle reading data from the
element on it’s own. We have to add another package called body-parser to gain this functionality.
npm install body-parser --save
Express allows us to add middlewares like body-parser to our application with the use method. You’ll hear the term middleware a lot when dealing with Express. These things are basically plugins that change the request or response object before they get handled by our application. Make sure you place body-parser before your CRUD handlers!
const express = require('express')const bodyParser= require('body-parser')const app = express()
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true}))
// All your handlers here...
The urlencoded method within body-parser tells body-parser to extract data from the
element and add them to the body property in the request object.
Now, you should be able to see everything in the form field within the req.body object. Try doing a console.log and see what it is!
app.post('/quotes', (req, res) => { console.log(req.body)})

Hmmm. Master Yoda has spoken! Let’s make sure we remember Yoda’s words. It’s important. We want to be able to retrieve it the next time we load our index page.
Enter the database, MongoDB.
MongoDB
We first have to install MongoDB through npm if we want to use it as our database.
npm install mongodb --save
Once installed, we can connect to MongoDB through the Mongo.Client‘s connect method as shown in the code below:
const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient
MongoClient.connect('link-to-mongodb', (err, database) => { // ... start the server})
The next part is to get the correct link to our database. Most people store their databases on cloud services like MongoLab. We’re going to do same as well.
So, go ahead and create an account with MongoLab. (It’s free).
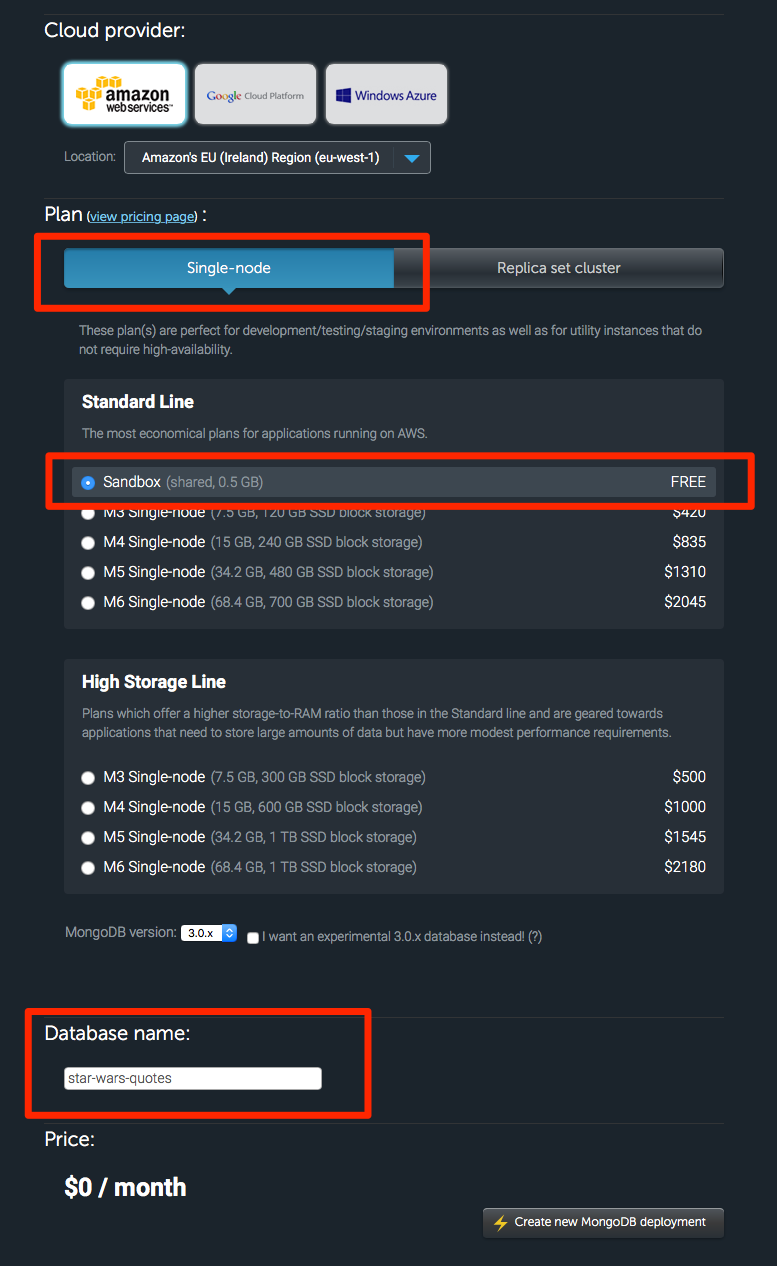
Once you’re done creating the deployment, head into it and create a database user and database password.
Note
Remember the database user and database password because you’re going to use it to connect the database you’ve just created.
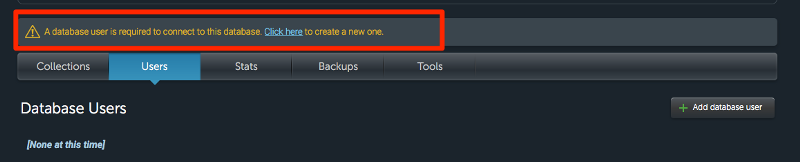
Finally, grab the MongoDB url and add it to your MongoClient.connect method.
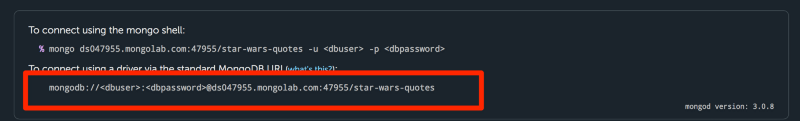
MongoClient.connect('your-mongodb-url', (err, database) => { // ... do something here})
Next, we want to start our servers only when the database is connected. Hence, let’s move app.listen into the connect method. We’re also going to create a db variable to allow us to use the database when we handle requests from the browser.
var db
MongoClient.connect('your-mongodb-url', (err, database) => {
if (err)
return console.log(err)
db = database
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('listening on 3000')
})
})
We’re done setting up MongoDB. Now, let’s create a quotes collection to store quotes for our application.
By the way, a collection is a named location to store stuff. You can create as many collections as you want. It can be things like “products”, “quotes”, “groceries”, or any other labels you choose.
We can create the quotes collection by using the string quotes while calling MongoDB’s db.collection() method. While creating the quotes collection, we can also save our first entry into MongoDB with the save method simultaneously.
Once we’re done saving, we have to redirect the user somewhere (or they’ll be stuck waiting forever for our server to move). In this case, we’re going to redirect them back to /, which causes their browsers to reload.
app.post('/quotes', (req, res) => {
db.collection('quotes')
.save(req.body, (err, result) => {
if (err) return console.log(err)
console.log('saved to database')
res.redirect('/')
})
})
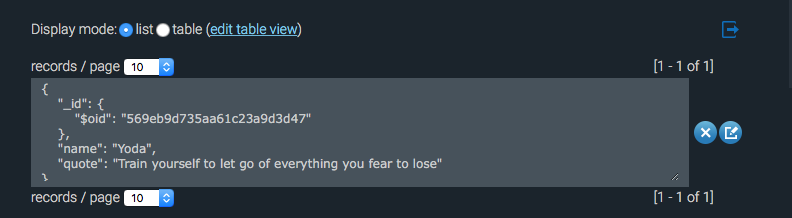
Whoohoo! Since we already have some quotes in the collection, why not try showing them to our user when they land on our page?
Showing quotes to users
We have to do two things to show the quotes stored in MongoLab to our users.
- Get quotes from MongoLab
- Use a template engine to display the quotes
Let’s go one step at a time.
We can get the quotes from MongoLab by using the find method that’s available in the collection method.
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
var cursor = db.collection('quotes').find()
})
console.log it out.The good news is, this cursor object contains all quotes from our database. It also contains a bunch of other properties and methods that allow us to work with data easily. One such method is the toArray method.
The toArray method takes in a callback function that allows us to do stuff with quotes we retrieved from MongoLab. Let’s try doing a console.log() for the results and see what we get!
db.collection('quotes')
.find()
.toArray(function(err, results) {
console.log(results) // send HTML file populated with quotes here})

Great! You now see an array of quotes (I only have one right now). We’ve completed the first part — getting data from MongoLab. The next part is to generate a HTML that contains all our quotes.
We can’t serve our index.html file and expect quotes to magically appear because there’s no way to add dynamic content to a HTML file. What we can do instead, is to use template engines to help us out. Some popular template engines include Jade, Embedded JavaScript and Nunjucks.
I’ve written extensively about the how and why of template engines in a separate post. You might want to check it out if you have no idea what template engines are. I personally use (and recommend) Nunjucks as my template engine of choice. Feel free to check out the post to find out why.
For this tutorial, we’re going to use Embedded JavaScript (ejs) as our template engine because it’s the easiest to start with. You’ll find it familiar from the get-go since you already know HTML and JavaScript.
We can use EJS by first installing it, then setting the view engine in Express to ejs.
npm install ejs --save
app.set('view engine', 'ejs')
Once the view engine is set, we can begin generating the HTML with our quotes. This process is also called rendering. We can use the render object built into the response object render to do so. It has the following syntax:
res.render(view, locals)
The first parameter, views, is the name of the file we’re rendering. This file must be placed within a views folder.
The second parameter, locals, is an object that passes data into the view.
Let’s first create an index.ejs file within the views folder so we can start populating data.
mkdir views
touch views/index.ejs
Now, place the following code within index.ejs.
<ul class="quotes">
<% for(var i=0; i<quotes.length; i++) {%>
<li class="quote">
<span><%= quotes[i].name %></span>
<span><%= quotes[i].quote %></span>
</li>
<% } %>
</ul>
See what I mean when I say you’ll find it familiar? In EJS, you can write JavaScript within <% and %> tags. You can also output JavaScript as strings if you use the <%= and %> tags.
Here, you can see that we’re basically looping through the quotes array and create strings with quotes[i].name and quotes[i].quote.
One more thing to do before we move on from the index.ejs file. Remember to copy the element from the index.html file into this file as well. The complete index.ejs file so far should be:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>MY APP</title>
</head>
<body>
May Node and Express be with you.
<ul class="quotes">
<% for(var i=0; i<quotes.length; i++) {%>
<li class="quote">
<span><%= quotes[i].name %></span>
<span><%= quotes[i].quote %></span>
</li>
<% } %>
</ul>
<form action="/quotes" method="POST">
<input type="text" placeholder="name" name="name">
<input type="text" placeholder="quote" name="quote">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Finally, we have to render this index.ejs file when handling the GET request. Here, we’re setting the results (an array) as the quotes array we used in index.ejs above.
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
db.collection('quotes')
.find()
.toArray((err, result) => {
if (err) return console.log(err)
// renders index.ejs
res.render('index.ejs', {quotes: result})
})
})
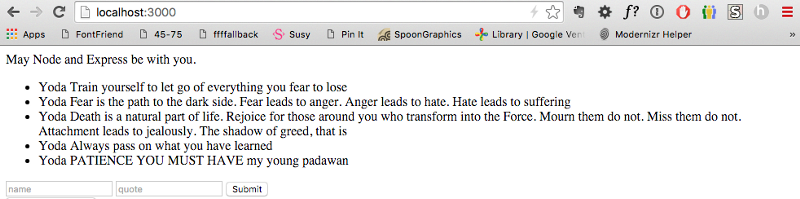
Um. You maybe only have one quote if you followed the tutorial step by step until this point. The reason I have multiple quotes is because I silently added more as I worked on the application.
Wrapping Up
We’ve covered a lot of ground in just 3000 words. Here are a few bullets to sum it all up. You have…
- Created an Express Server
- Learned to execute CREATE and READ operations
- Learned to save and read from MongoDB
- Learned to use a template engine like Embedded JS.
There are two more operations to go, but we’ll leave it to the next post. Catch you there!
This article first appeared on my blog at zell-weekeat.com. Check it out if you want more articles like this