Troubleshooting 관련
The pipeline is not starting
You have created the YML file with your pipeline but nothing happens. Now what?
First, check if you have named the pipeline exactly .gitlab-ci.yml and is located at the root of your project. This is not the same as gitlab-ci.yml , .gitlab-ci.yaml or anything else.
Most people enable Auto DevOps — this is rarely the solution you are looking for. Auto DevOps is meant to create the pipeline for you. Since you already have a pipeline, enabling Auto DevOps is NOT the solution.
Other common reasons for this problem include:
- the
.gitlab-ci.ymlhas been added to a subdirectory; - no commits have been pushed to the remote server;
- there are no runners to execute the job;
Found errors in your .gitlab-ci.yml: stages config should be an array of strings
stages:
-build
-test
This is a common mistake when you have no added a space after the hyphen sign —.
Mapping values are not allowed in this context at line X column Y
This error is hard to spot. Take a look at the pipeline below:
stages
- build
- test
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Building"
artifacts:
paths:
- build/
tests:
stage: test
script:
- echo "Testing"
The error “(<unknown>): mapping values are not allowed in this context at line 5 column 6” is having us look at line 5, when the problem is actually inside the first line. stages defines a list, and must be followed by a colon, like stages: .
Config contains unknown keys: path
Does your pipeline look like this:
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Building"
artifacts:
path:
- build/
The way you specify the build folder as an artifact is by setting the paths property. This is a plural as it can specify a list of files or folders which will be published as artifacts.
<some job name> config contains unknown keys: paths
build the car:
stage: build
script:
- mkdir build
- cd build
- touch car.txt
- echo "chassis" >> car.txt
- echo "Engine" >> car.txt
- echo "wheels" >> car.txt
artifacts:
paths:
- build/
This is a typical case of improper indentation. paths is a property of artifacts . Add two spaces before paths and the problem is solved.
root config contains unknown keys: <some job name>
This is one of the most confusing errors out there. Typically, the error is pointing you in the right direction, but not this time. Have a look at the following configuration:
...
deploy review:
stage: deploy review
only:
- merge requests
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: none
script:
- echo "Deploying on review"
- sh ./deploy.sh
...
Can you spot the issue? GitLab is not recognizing the configuration deploy reviewas a job. The problem here is that this job configuration is missing the script block. Because the script is not properly indented, it has been defined as a variable.
(<unknown>): did not find expected key while parsing a block mapping at line 1 column 1
stages:
- build
- test
build the car:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Build"
test the car:
stage: test
script:
- echo "Test"
What seems to be the issue here? I can assure you there is no issue on line 1 column 1. The problem is bad indentation. The echo command in the first job is not properly indented. The second job is also not properly indented. This is how the configuration should look like:
stages:
- build
- test
build the car:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Build"
test the car:
stage: test
script:
- echo "Test"
This job is stuck because you don't have any active runners that can run this job. Go to Runners page.
If you use the shared runners from GitLab.com, this will get fixed automatically after a while. Depending on the load, the job might wait a bit.
(<unknown>): mapping values are not allowed in this context at line 1 column 12
This is a common error if you somehow add a space when specifying the version of the Docker image you want to use. Example
image: node: 12
It should be:
image: node:12
/bin/bash: line <line>: <some tool>: command not found
The first step in resolving this issue is understanding which Docker image is being used by the job.
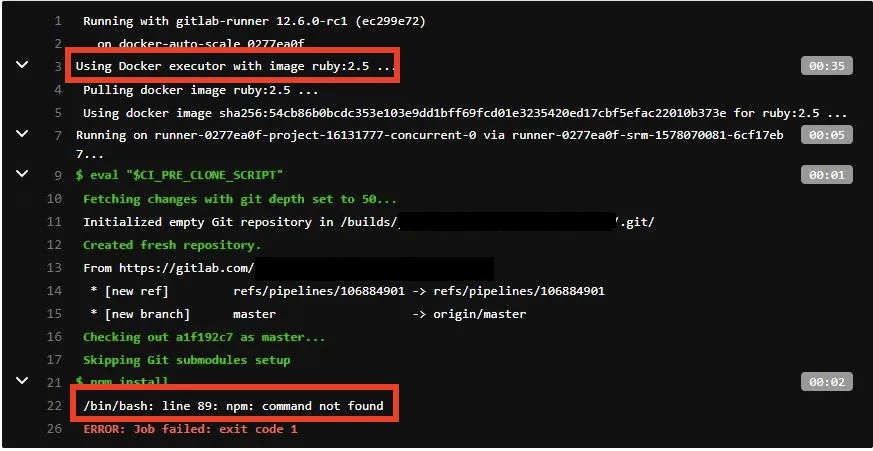
If you don't specify a Docker image for your job, the GitLab runner executing your job will use the default image, in this case: ruby:2.5 . The problem with this is that this Docker container does not have node and npm installed, and this is why the job is failing.
The easiest solution is to use a Docker image that already has the tools you need, like node.
If you still wish to use the image (whatever that image is), you need to use the package manager to install any missing tools you need.
ERROR: Job failed: exit code 1
This is a very generic error. You need to look at the console logs from the beginning to the end to understand which commands have been executed and what has happened.
Understanding your logs is key to understanding your pipeline.
If something does not work, try breaking down the job into smaller parts to identify the root cause for your error.
Once you have identified that error, search for that specific error.
If you want to learn how to build pipelines in Gitlab CI, I have created an online course that starts with the basics of Gitlab CI and YAML and helps you understand the fundamentals of CI/CD. Learn more about the course.
Environment variables are not resolved Quite often we set environment variables in GitLab to avoid storing them inside our Git repositories. To see if they are working, add the following line of code in your scripts:
- echo $SOME_VARIABLE
Try to see if this works both within the main branch, was well as in the merge requests. If it only works on the main branch, re-check your configuration.
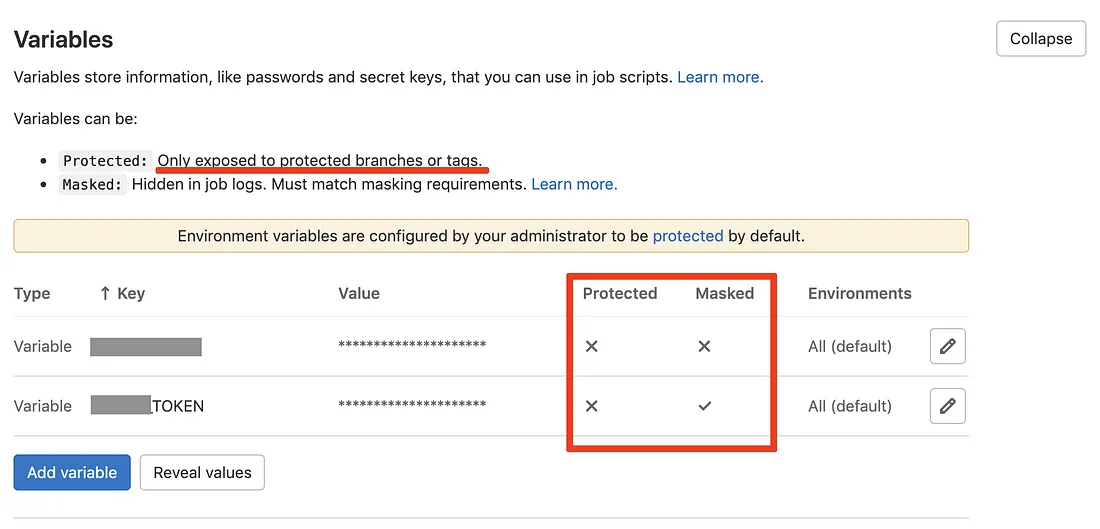
Make sure you understand the difference between a protected variable and a masked variable. If you have a variable which you need in Merge Requests / branches, this variable needs to be unprotected, as most likely the branch itself is unprotected.
