m=γm0,⟨m0:mass at rest⟩
E=W=∫F⋅dx=∫(ma)⋅dx=∫m(dtdv)⋅x=∫m(dtdx)dv=∫m(v)(dv)=m(2v2)=21mv2;
E=W=∫F⋅dx=∫(dtdp)dx,=∫dtd(p)dx=∫dtd(γm0v)=∫m0(γdtdv+vdtdγ)=⋯⟨F=dtdp⟩
⎩⎨⎧γdtdγ=(1−c2v2)−21;=dtd(γ)=dtd(1−c2v2)−21=(−21)(1−c2v2)−23[(−c22v)(dtdv)]=c2vγ3dtdv⎭⎬⎫
E=∫m0(γdtdv+v(c2vγ3dtdv))dx=∫m0(γdv+c2v2γ3dv)dtdx=∫m0γdv(1+c2v2γ2)dtdx
⎩⎨⎧1+c2v2γ2=1+(c2v2)(c2−v2c2)=1+c2−v2v2=(c2−v2v2)+(c2−v2c2−v2)=c2−v2c2=γ2⎭⎬⎫
E=∫m0γ(γ2)dv(v)=∫m0γ3vdv,⟨dtdγ=c2vγ3dtdv;dγ=c2vγ3dv⟩=∫m0(c2)dγ=m0c2∫dγ=γm0c2;
∴E=γm0c2
Give the lower and upper bounds for this integral
E=m0c2(1−c2v2)−210v=m0c2(1−c2(v)2)−21−m0c2(1−c2(0)2)−21=m0c2γ−m0c2=(γ−1)m0c2;
given velocity "close" to speed of light, the kinetic energy is denoted,
K=γm0c2−m0c2=Etotal−Erest=(γ−1)m0c2
to see if this equation holds true in classical physics.
⎩⎨⎧v≪c,Binomial Expansionγ≈1+21c2v2⎭⎬⎫
K≈[(1+21c2v2)−1]m0c2=21m0v2
mm2m02c2(m02c2)(c2)(m0c2)2(mc2)2(Etotal)2=γm0;=γ2m02=(c2−v2c2)m02;=m2(c2−v2)=m2c2−m2v2;=(c2)(m2c2−m2v2);=(mc2)2−m2c2v2;=m2c2v2+(m0c2)2;⟨E=m0c2⟩⟨p=mv⟩=(pc)2+(Erest)2
Basically he proposed that in special relativity, electrons can have both a positive charge and negative energy.
Q: how is it possible to have an electron with energy that is positively charged?
E=mc3
pˉ+p→many
proton:
mp=938.3MeV/c2
neutron:
mn=939.6MeV/c2
deutreon:
md=(mp+mn)=(939.6+939.6)=1877.05MeV/c2
Q: But from the investigation, this is simply shown not true. Will it be larger or smaller?
A: it is LESS .
md=1875.6MeV/c2
What happened? See here.
- pioneer of photography.
- We used to work for pottery shop owned by his dad, Josiah Wedgwood.
- Discovery: Regardless of shape, thing glowed in the same colord and at the same temperature (generally high).
AE∝RT(f);⟨power fluxRT(f)=1[m2W⋅f1]=[]f1⟩
- black body
- black body tends to absorb more heat.
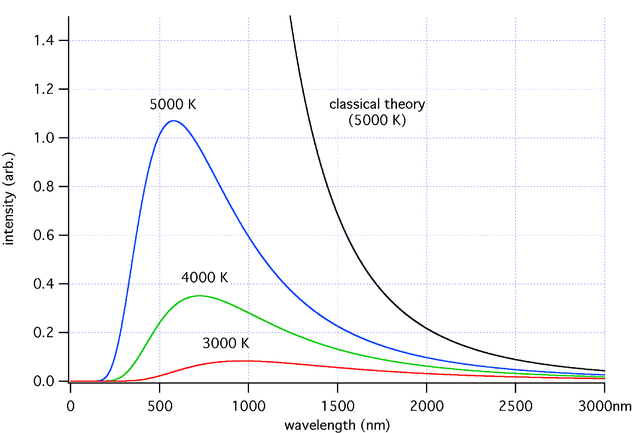 black body radiation graph
black body radiation graph⟨power fluxRT(f)=1[m2W⋅f1]⟩
RT(f)∴RT(f)=t⋅AE⋅f1=tE⋅(volL)⋅f1=volE⋅tL⋅f1=energy density(ρT(t))(v)(f1)∝(ρT(t))⋅f1
y1y2=Asin(kx+ωt)=Asin(kx−ωt)
⎩⎨⎧yϕkxx=Asinϕ=kx+ωt,=d±ωt=kd±kωt,=C±vt;⟨k:wave #⟩⟨v=kω⟩⎭⎬⎫
y1+y2=Asin(kx+ωt)+Asin(kx−ωt)⟨sin(a)+sin(b)=2[sin(21(a+b))cos(21(a−b))]⟩=2Asin(2(kx+ωt)+(kx−ωt))cos(2(kx+ωt)−(kx−ωt))=2Asin(kx)cos(ωt)
⎩⎨⎧kx(λ2π)Lλ=nπ;=nπ;=n2L;⎭⎬⎫
ffcfc=λv=(2Ln)v=2LnvEM Wave (1D)=(2Lc)n;EM Wave (3D)=(2Lc)(nx)2+(ny)2+(nz)2;⟨n:mode #L:size of capacity⟩
For EM wave
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_body

