Dictionaries
Dictionaries 관련
As you've seen, Swift arrays are a collection where you access each item using a numerical index, such as songs[0]. Dictionaries are another common type of collection, but they differ from arrays because they let you access values based on a key you specify.
To give you an example, let's imagine how we might store data about a person in an array:
var person = ["Taylor", "Alison", "Swift", "December", "taylorswift.com"]
To read out that person's middle name, we'd use person[1], and to read out the month they were born we'd use person[3]. This has a few problems, not least that it's difficult to remember what index number is assigned to each value in the array! And what happens if the person has no middle name? Chances are all the other values would move down one place, causing chaos in your code.
With dictionaries we can re-write this to be far more sensible, because rather than arbitrary numbers you get to read and write values using a key you specify. For example:
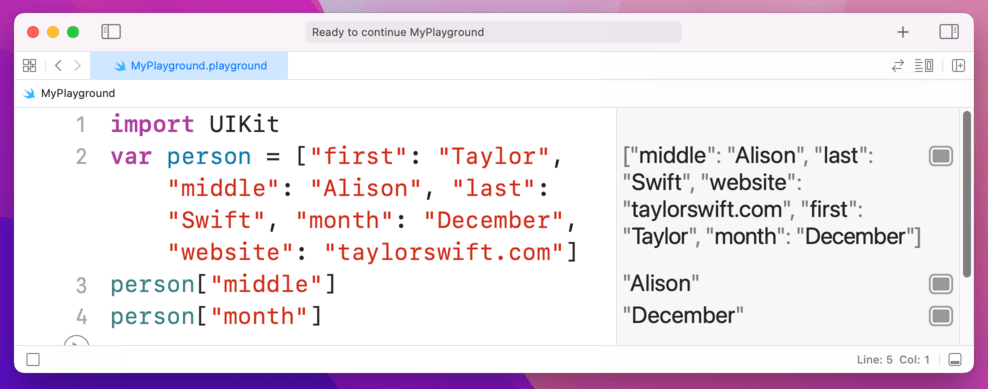
var person = ["first": "Taylor", "middle": "Alison", "last": "Swift", "month": "December", "website": "taylorswift.com"]
person["middle"]
person["month"]
It might help if I use lots of whitespace to break up the dictionary on your screen, like this:
var person = [
"first": "Taylor",
"middle": "Alison",
"last": "Swift",
"month": "December",
"website": "taylorswift.com"
]
person["middle"]
person["month"]
As you can see, when you make a dictionary you write its key, then a colon, then its value. You can then read any value from the dictionary just by knowing its key, which is much easier to work with.
As with arrays, you can store a wide variety of values inside dictionaries, although the keys are most commonly strings.