
Building Our Python Backend
Building Our Python Backend 관련
For this tutorial I will be using macOS, and the commands should also work on Linux. If you’re a Windows user, most of the commands should work (although there are some differences like activating a Python environment). You can find the correct commands by searching if need be - and you’ll know if your terminal gives you errors when trying to run a command.
Creating An Account On Groq Cloud
As mentioned earlier, we will use Meta’s LLaMA 3 via Groq Cloud, which is ideal. So, first, we have to create an account on Groq Cloud, as shown here.

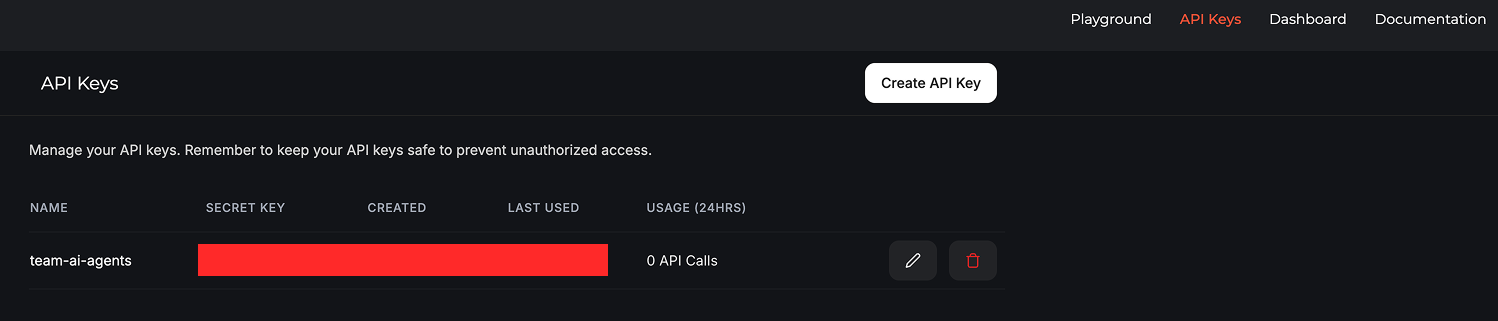
Once you have created an account on Groq Cloud, go to the API Keys page and create an API Key as shown in this example. I gave mine the name team-ai-agents:
You should have an API Key that looks like this example, so make sure that you save it somewhere safe - we will need it later.
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
Setting Up Our Python Project
Ok, now let's quickly set up our project. Navigate to a location on your computer, like the desktop, and create a folder called ai-agent-app. cd into the project folder and get ready - we’re going to start building our backend using Python.
I recommend installing agno and groq locally in a Python virtual environment. First, use this terminal command to setup a Python virtual environment inside of your ai-agent-app folder:
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
cd venv
Note: depending on your local Python environment, you might need to use either the python or python3 command for running Python commands. In my environment and examples, I use python3, so adjust the command to suit your needs.
The same applies when using either pip or pip3 when installing Python packages. You can check to see which version of Python and pip you have installed with the python --version, python3 --version , pip --version and pip3 --version commands in your terminal window.
The above command should create a venv folder inside of your ai-agent-app folder. This will be your REST backend with all of your API endpoints which your React frontend will use later on in this tutorial. Your Python virtual environment has also been activated.
To activate and deactivate your Python environment, you can use these commands:
::: tab
@tab:active
venv\Scripts\activate
@tab ,
source venv/bin/activate
:::
conda deactivate
At this point, its a good idea to open the project in your code editor. Now you’ll need to install agno and groq using pip alongside a few other packages: flask, requests, and python-dotenv. You need these packages for setting up your server environment, so go ahead and install them all with this command:
pip install agno
pip install groq
pip install flask
pip install flask_cors
pip install requests
pip install python-dotenv
With these Python packages installed, you’re now ready to set up your API for this project. We’ll be using the Python web application framework Flask, along with the CORS package so that we can access the server anywhere. At the same time, we’ll also use the requests module, which allows us to send HTTP requests using Python.
Note that you’ll also need a .env file for your API keys, so make sure you have installed the python-dotenv package in your Python environment, although in some cases, it's installed automatically.
Working On The Python Codebase
Alright, time to make a start on the codebase. But first, let's generate all of the files for your project. You can do this simply by running the run script I created for the project. Run this command in the venv folder:
mkdir agents
touch .env main.py
cd agents
touch __init__.py base_agent.py career_agent.py client_agent.py project_agent.py research_agent.py welcome_agent.py
With this script, you should now have:
- Created a
.envfile for your API Keys - Created an agents folder with all of the files for creating your different AI agents
- Created a
main.pyfile, which will be the main project file for your entire backend app
Ok, your files are set. All that’s left is to add the codebase, and the backend is complete. Let's start with the .env file, as it only needs one line of code and that is for your API key. See my example and update it with your own API Key:
GROQ_API_KEY="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"
Your application now has an API key, which gives you access to Groq Cloud. Now let’s start to add the code for all the various AI agents. The first file we’ll work on will be the __init__.py which holds the imports for all of the AI agent files.
Add this code to the file:
from agents.welcome_agent import WelcomeAgent
from agents.project_agent import ProjectAgent
from agents.career_agent import CareerAgent
from agents.client_agent import ClientAgent
from agents.research_agent import ResearchAgent
# Export all agents
__all__ = ['WelcomeAgent', 'ProjectAgent', 'CareerAgent', 'ClientAgent', 'ResearchAgent']
As you can see, all of the classes for the AI agents will be imported and exported from here so you can use them in your main.py file later.
Ok, good. Now, we have 6 AI agent files to work on, beginning with the base_agent.py file.
Make sure that you add this code to the file:
from agno.agent import Agent
from agno.models.groq import Groq
import os
class BaseAgent:
def __init__(self, name, description, avatar="default_avatar.png"):
self.name = name
self.description = description
self.avatar = avatar
self.model = Groq(id="llama-3.3-70b-versatile")
self.agent = Agent(model=self.model, markdown=True)
def get_response(self, query, stream=False):
return self.agent.get_response(query, stream=stream)
def print_response(self, query, stream=True):
return self.agent.print_response(query, stream=stream)
This class uses the agno framework to create AI agents powered by Groq's LLama 3.3 70B model, which is free to use with some usage restrictions for API calls. This should be fine for your project. It provides the basic structure that other specialised agents in the application can inherit from and extend with domain-specific functionality.
The model we chose is available on the Groq Cloud platform, and we can change it if we want to. Each model has pros and cons, and a cut-off date for how up-to-date it is, so you can expect to get different results. Just keep in mind that using an up to date LLM like OpenAI will provide better results, but you might have to pay for it.
The next file we will work on will be the <FontIcon icon="fa-brands fa-python"/>career_agent.py file.
And this is this code required for it:
from agents.base_agent import BaseAgent
class CareerAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
name="CareerGuide",
description="I'm the career specialist. I can provide information about skills, experience, and job suitability.",
avatar="career_avatar.png"
)
self.skills = {
"languages": ["Python", "JavaScript", "TypeScript", "Java", "SQL"],
"frameworks": ["React", "Vue.js", "Node.js", "Django", "Flask", "Spring Boot"],
"tools": ["Git", "Docker", "AWS", "Azure", "CI/CD", "Kubernetes"],
"soft_skills": ["Team leadership", "Project management", "Agile methodologies", "Technical writing", "Client communication"]
}
self.experience = [
{
"title": "Senior Full Stack Developer",
"company": "Tech Innovations Inc.",
"period": "2020-Present",
"responsibilities": [
"Led development of cloud-based SaaS platform",
"Managed team of 5 developers",
"Implemented CI/CD pipeline reducing deployment time by 40%",
"Architected microservices infrastructure"
]
},
{
"title": "Full Stack Developer",
"company": "WebSolutions Co.",
"period": "2017-2020",
"responsibilities": [
"Developed responsive web applications using React and Node.js",
"Implemented RESTful APIs and database schemas",
"Collaborated with UX/UI designers to implement user-friendly interfaces",
"Participated in code reviews and mentored junior developers"
]
},
{
"title": "Junior Developer",
"company": "StartUp Labs",
"period": "2015-2017",
"responsibilities": [
"Built and maintained client websites",
"Developed custom WordPress plugins",
"Implemented responsive designs and cross-browser compatibility",
"Assisted in database design and optimization"
]
}
]
def get_skills_summary(self):
prompt = f"""
Generate a professional summary of the following skills for a portfolio website:
Programming Languages: {', '.join(self.skills['languages'])}
Frameworks & Libraries: {', '.join(self.skills['frameworks'])}
Tools & Platforms: {', '.join(self.skills['tools'])}
Soft Skills: {', '.join(self.skills['soft_skills'])}
Format the response in markdown with appropriate sections and highlights.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def get_experience_summary(self):
experience_text = "# Work Experience\n\n"
for job in self.experience:
experience_text += f"## {job['title']} at {job['company']}\n"
experience_text += f"**{job['period']}**\n\n"
experience_text += "**Responsibilities:**\n"
for resp in job['responsibilities']:
experience_text += f"- {resp}\n"
experience_text += "\n"
prompt = f"""
Based on the following work experience, generate a professional career summary for a portfolio website:
{experience_text}
Highlight career progression, key achievements, and growth. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def assess_job_fit(self, job_description):
skills_flat = []
for skill_category in self.skills.values():
skills_flat.extend(skill_category)
experience_flat = []
for job in self.experience:
experience_flat.extend(job['responsibilities'])
prompt = f"""
Assess the fit for the following job description based on the skills and experience provided:
Job Description:
{job_description}
Skills:
{', '.join(skills_flat)}
Experience:
{' '.join(experience_flat)}
Provide an analysis of strengths, potential gaps, and overall suitability for the role. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
This agent is designed to help users with career-related tasks such as:
- Creating professional summaries of technical and soft skills
- Generating career narratives based on work experience
- Evaluating job fit by comparing skills and experience against job descriptions
The agent uses the LLM capabilities of the base agent (using Groq's LLama 3.3 70B model) to generate natural language responses that are formatted in markdown, making them suitable for inclusion in portfolio websites, résumés, or job applications. This file has sample career data, and in a real implementation, this would come from a database
Ok time for the next AI agent - this time it’s client_agent.py, which receives this code:
from agents.base_agent import BaseAgent
class ClientAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
name="BusinessAdvisor",
description="I'm the client specialist. I can provide information about services, pricing, and project details.",
avatar="client_avatar.png"
)
self.services = {
"web_development": {
"name": "Web Development",
"description": "Custom web application development using modern frameworks and best practices.",
"pricing_model": "Project-based or hourly",
"price_range": "$5,000 - $50,000 depending on complexity",
"timeline": "4-12 weeks depending on scope",
"technologies": ["React", "Vue.js", "Node.js", "Django", "Flask"]
},
"mobile_development": {
"name": "Mobile App Development",
"description": "Native and cross-platform mobile application development for iOS and Android.",
"pricing_model": "Project-based",
"price_range": "$8,000 - $60,000 depending on complexity",
"timeline": "6-16 weeks depending on scope",
"technologies": ["React Native", "Flutter", "Swift", "Kotlin"]
},
"consulting": {
"name": "Technical Consulting",
"description": "Expert advice on architecture, technology stack, and development practices.",
"pricing_model": "Hourly",
"price_range": "$150 - $250 per hour",
"timeline": "Ongoing or as needed",
"technologies": ["Various based on client needs"]
}
}
self.process = [
"Initial consultation to understand requirements",
"Proposal and quote preparation",
"Contract signing and project kickoff",
"Design and prototyping phase",
"Development sprints with regular client feedback",
"Testing and quality assurance",
"Deployment and launch",
"Post-launch support and maintenance"
]
def get_services_overview(self):
services_text = "# Services Offered\n\n"
for service_id, service in self.services.items():
services_text += f"## {service['name']}\n"
services_text += f"{service['description']}\n\n"
services_text += f"**Pricing Model**: {service['pricing_model']}\n"
services_text += f"**Price Range**: {service['price_range']}\n"
services_text += f"**Timeline**: {service['timeline']}\n"
services_text += f"**Technologies**: {', '.join(service['technologies'])}\n\n"
prompt = f"""
Generate a professional overview of the following services for a programmer's portfolio website:
{services_text}
Format the response in markdown with appropriate sections and highlights.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def get_service_details(self, service_id):
if service_id in self.services:
service = self.services[service_id]
prompt = f"""
Generate a detailed description for the following service:
Service Name: {service['name']}
Description: {service['description']}
Pricing Model: {service['pricing_model']}
Price Range: {service['price_range']}
Timeline: {service['timeline']}
Technologies: {', '.join(service['technologies'])}
Include information about the value proposition, typical deliverables, and client benefits. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
else:
return "Service not found. Please check the service ID and try again."
def explain_process(self):
process_text = "# Client Engagement Process\n\n"
for i, step in enumerate(self.process, 1):
process_text += f"## Step {i}: {step}\n\n"
prompt = f"""
Based on the following client engagement process, generate a detailed explanation for potential clients:
{process_text}
For each step, provide a brief explanation of what happens, what the client can expect, and any deliverables. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def generate_proposal(self, project_description):
prompt = f"""
Generate a professional project proposal based on the following client requirements:
Project Description:
{project_description}
Include the following sections:
1. Project Understanding
2. Proposed Approach
3. Estimated Timeline
4. Estimated Budget Range
5. Next Steps
Base your proposal on the services and processes described in the portfolio. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
This agent is designed to help users with client and business-related tasks such as:
- Providing overviews of available services for marketing materials
- Generating detailed service descriptions for specific offerings
- Explaining the client engagement process to potential clients
- Creating customised project proposals based on client requirements
The agent also uses the LLM capabilities of the base agent (using Groq's LLama 3.3 70B model) to generate professional, business-oriented content formatted in markdown. Like before, this file also has sample service data.
Now we can start to work on the project_agent.py file and add this code to its codebase:
from agents.base_agent import BaseAgent
class ProjectAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
name="TechExpert",
description="I'm the project specialist. I can provide detailed information about any project in this portfolio.",
avatar="project_avatar.png"
)
self.projects = {
"project1": {
"name": "E-commerce Platform",
"tech_stack": ["React", "Node.js", "MongoDB", "Express"],
"description": "A full-stack e-commerce platform with user authentication, product catalog, shopping cart, and payment processing.",
"highlights": ["Responsive design", "RESTful API", "Stripe integration", "JWT authentication"],
"github_link": "https://github.com/username/ecommerce-platform",
"demo_link": "https://ecommerce-demo.example.com"
},
"project2": {
"name": "Task Management App",
"tech_stack": ["Vue.js", "Firebase", "Tailwind CSS"],
"description": "A real-time task management application with collaborative features, notifications, and progress tracking.",
"highlights": ["Real-time updates", "User collaboration", "Drag-and-drop interface", "Progressive Web App"],
"github_link": "https://github.com/username/task-manager",
"demo_link": "https://taskmanager-demo.example.com"
},
"project3": {
"name": "Data Visualization Dashboard",
"tech_stack": ["Python", "Django", "D3.js", "PostgreSQL"],
"description": "An interactive dashboard for visualizing complex datasets with filtering, sorting, and export capabilities.",
"highlights": ["Interactive charts", "Data filtering", "CSV/PDF export", "Responsive design"],
"github_link": "https://github.com/username/data-dashboard",
"demo_link": "https://dataviz-demo.example.com"
}
}
def get_project_list(self):
project_list = "# Available Projects\n\n"
for project_id, project in self.projects.items():
project_list += f"## {project['name']}\n"
project_list += f"**Tech Stack**: {', '.join(project['tech_stack'])}\n"
project_list += f"{project['description']}\n\n"
return project_list
def get_project_details(self, project_id):
if project_id in self.projects:
project = self.projects[project_id]
prompt = f"""
Generate a detailed description for the following project:
Project Name: {project['name']}
Tech Stack: {', '.join(project['tech_stack'])}
Description: {project['description']}
Highlights: {', '.join(project['highlights'])}
GitHub: {project['github_link']}
Demo: {project['demo_link']}
Include technical details about implementation challenges and solutions. Format the response in markdown.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
else:
return "Project not found. Please check the project ID and try again."
def answer_technical_question(self, project_id, question):
if project_id in self.projects:
project = self.projects[project_id]
prompt = f"""
Answer the following technical question about this project:
Project Name: {project['name']}
Tech Stack: {', '.join(project['tech_stack'])}
Description: {project['description']}
Highlights: {', '.join(project['highlights'])}
Question: {question}
Provide a detailed technical answer with code examples if relevant.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
else:
return "Project not found. Please check the project ID and try again."
This agent is designed to help users with project-related tasks such as:
- Providing an overview of all projects in a portfolio
- Generating detailed descriptions of specific projects
- Answering technical questions about implementation details
The agent, like in the previous examples, uses the LLM capabilities of the base agent (using Groq's LLama 3.3 70B model) to generate technical, project-oriented content formatted in markdown. This is good for technical documentation, or when responding to inquiries about project implementations. We’re using mock data here as opposed to a database.
With that file completed, we have two left. The next is the research_agent.py file, so go ahead and add this code:
from agents.base_agent import BaseAgent
import requests
import os
import json
class ResearchAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
name="ResearchAssistant",
description="I'm the research specialist. I can search the web for information about technologies, trends, and industry news.",
avatar="research_avatar.png"
)
self.api_key = os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY")
def search_web(self, query):
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"model": "llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful research assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Search the web for: {query}"}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "web_search"
}
]
}
try:
response = requests.post(
"https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/chat/completions",
headers=headers,
json=payload
)
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
return result["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
else:
return f"Error searching the web: {response.status_code} - {response.text}"
except Exception as e:
return f"Error searching the web: {str(e)}"
def research_technology(self, technology):
query = f"latest developments and best practices for {technology} in software development"
search_results = self.search_web(query)
prompt = f"""
Based on the following search results about {technology}, provide a concise summary of:
1. What it is
2. Current state and popularity
3. Key features and benefits
4. Common use cases
5. Future trends
Search Results:
{search_results}
Format the response in markdown with appropriate sections.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def compare_technologies(self, tech1, tech2):
query = f"comparison between {tech1} and {tech2} for software development"
search_results = self.search_web(query)
prompt = f"""
Based on the following search results comparing {tech1} and {tech2}, provide a detailed comparison including:
6. Core differences
7. Performance considerations
8. Learning curve
9. Community support
10. Use case recommendations
Search Results:
{search_results}
Format the response in markdown with a comparison table and explanatory text.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
def get_industry_trends(self):
query = "latest trends in software development industry"
search_results = self.search_web(query)
prompt = f"""
Based on the following search results about software development trends, provide a summary of:
11. Emerging technologies
12. Industry shifts
13. In-demand skills
14. Future predictions
Search Results:
{search_results}
Format the response in markdown with appropriate sections and highlights.
"""
return self.get_response(prompt)
This agent is designed to help users with research-related tasks such as:
- Researching specific technologies to understand their features, benefits, and use cases
- Comparing different technologies to make informed decisions
- Staying updated on industry trends and emerging technologies
What makes this agent unique compared to the other agents is that it actively fetches real-time information from the web using the Groq Toolhouse API's web search capability instead of relying solely on pre-defined data or the LLM's training data. This allows it to provide more current and comprehensive information about rapidly evolving technology topics.
Ok, now we have one last AI agent to create and it’s the welcome_agent.py file. Add this code to the file:
from agents.base_agent import BaseAgent
class WelcomeAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
name="Greeter",
description="I'm the welcome agent for this portfolio. I can help guide you to the right section based on your interests.",
avatar="welcome_avatar.png"
)
def greet(self, visitor_type=None):
if visitor_type == "employer":
return self.get_response(
"Generate a friendly, professional greeting for a potential employer visiting a programmer's portfolio website. "
"Mention that they can explore the Projects section to see technical skills and the Career section for professional experience."
)
elif visitor_type == "client":
return self.get_response(
"Generate a friendly, business-oriented greeting for a potential client visiting a programmer's portfolio website. "
"Mention that they can check out the Projects section for examples of past work and the Client section for service details."
)
elif visitor_type == "fellow_programmer":
return self.get_response(
"Generate a friendly, casual greeting for a fellow programmer visiting a portfolio website. "
"Mention that they can explore the Projects section for technical details and code samples."
)
else:
return self.get_response(
"Generate a friendly, general greeting for a visitor to a programmer's portfolio website. "
"Ask if they are an employer, client, or fellow programmer to provide more tailored information."
)
def suggest_section(self, interest):
prompt = f"Based on a visitor expressing interest in '{interest}', suggest which section of a programmer's portfolio they should visit. Options include: Projects, Career, Client Work, About Me, Contact. Explain why in 1-2 sentences."
return self.get_response(prompt)
This agent is designed to serve as the initial point of contact for visitors to a portfolio website, providing:
- Personalised greetings based on visitor type
- Guidance to relevant sections based on specific interests
- A friendly, conversational introduction to the portfolio
The WelcomeAgent is simpler than some of the other agents we've looked at because it focuses on creating a positive first impression and helping visitors navigate to the content most relevant to their needs. It uses the LLM capabilities of the base agent to generate natural, contextually appropriate responses.
Ok good - your backend API is almost ready. You just have one last file to work on: the main.py file that completes your codebase. This file is quite big, so I will split it into three parts. You’ll need to copy and paste each section into the file. If you have not done so already, its worth installing the Python extension for VS Code as this has debugging, linting, and formatting for Python files.
Alright, here is the first part of the codebase for our main.py file:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import json
import requests
from flask_cors import CORS
load_dotenv()
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)
class BaseAgent:
def __init__(self, name, description):
self.name = name
self.description = description
self.api_key = os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY")
def get_response(self, prompt):
try:
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
data = {
"model": "llama3-8b-8192",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": f"You are {self.name}, {self.description}. Respond in a helpful, concise, and professional manner."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 500
}
response = requests.post(
"https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/chat/completions",
headers=headers,
json=data
)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
else:
return f"Error: {response.status_code} - {response.text}"
except Exception as e:
return f"An error occurred: {str(e)}"
class WelcomeAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"WelcomeAgent",
"a welcome specialist who greets visitors and helps them navigate the portfolio website"
)
def greet(self, visitor_type=None):
if visitor_type == "employer":
return self.get_response("Generate a warm welcome message for an employer visiting a programmer's portfolio website. Suggest they check out the Projects and Career sections.")
elif visitor_type == "client":
return self.get_response("Generate a warm welcome message for a potential client visiting a programmer's portfolio website. Suggest they check out the Services section.")
elif visitor_type == "fellow_programmer":
return self.get_response("Generate a warm welcome message for a fellow programmer visiting a programmer's portfolio website. Suggest they check out the Projects and Research sections.")
else:
return self.get_response("Generate a general welcome message for a visitor to a programmer's portfolio website. Ask if they are an employer, client, or fellow programmer.")
def suggest_section(self, interest):
return self.get_response(f"A visitor to my portfolio website has expressed interest in {interest}. Suggest which section(s) of the website they should visit based on this interest.")
class ProjectAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"ProjectAgent",
"a project specialist who provides detailed information about the programmer's projects"
)
def get_project_list(self):
return self.get_response("Generate a list of 3-5 impressive software development projects that could be in a programmer's portfolio. Include a brief description for each.")
def get_project_details(self, project_id):
project_prompts = {
"project1": "Describe in detail an e-commerce platform project for a programmer's portfolio. Include technologies used, challenges overcome, and key features.",
"project2": "Describe in detail a task management application project for a programmer's portfolio. Include technologies used, challenges overcome, and key features.",
"project3": "Describe in detail a data visualization dashboard project for a programmer's portfolio. Include technologies used, challenges overcome, and key features."
}
prompt = project_prompts.get(
project_id, f"Describe a project called {project_id} in detail.")
return self.get_response(prompt)
def answer_technical_question(self, project_id, question):
return self.get_response(f"Answer this technical question about a project: '{question}'. The project is {project_id}.")
This part of the code has your imports, set up, and some greetings for the AI agent.
Now for part two, add this code to the file underneath the first code you added:
class CareerAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"CareerAgent",
"a career specialist who provides information about the programmer's skills and experience"
)
def get_skills_summary(self):
return self.get_response("Generate a comprehensive summary of technical and professional skills for a full-stack developer's portfolio.")
def get_experience_summary(self):
return self.get_response("Generate a summary of work experience for a full-stack developer with 5+ years of experience.")
def assess_job_fit(self, job_description):
return self.get_response(f"Assess how well a full-stack developer with 5+ years of experience would fit this job description: '{job_description}'. Highlight matching skills and experience.")
class ClientAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"ClientAgent",
"a client specialist who provides information about services, pricing, and the client engagement process"
)
def get_services_overview(self):
return self.get_response("Generate an overview of services that a freelance full-stack developer might offer to clients.")
def get_service_details(self, service_type):
service_prompts = {
"web_development": "Describe web development services offered by a freelance full-stack developer, including technologies, pricing range, and typical timeline.",
"mobile_development": "Describe mobile app development services offered by a freelance full-stack developer, including technologies, pricing range, and typical timeline.",
"consulting": "Describe technical consulting services offered by a freelance full-stack developer, including areas of expertise, hourly rate range, and engagement model."
}
prompt = service_prompts.get(
service_type, f"Describe {service_type} services in detail.")
return self.get_response(prompt)
def explain_process(self):
return self.get_response("Explain the client engagement process for a freelance full-stack developer, from initial consultation to project delivery.")
def generate_proposal(self, project_description):
return self.get_response(f"Generate a project proposal for this client request: '{project_description}'. Include estimated timeline, cost range, and approach.")
class ResearchAgent(BaseAgent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"ResearchAgent",
"a research specialist who provides information about technologies, trends, and industry news"
)
def search_web(self, query):
return self.get_response(f"Provide information about '{query}' as if you've just searched the web for the latest information. Include key points and insights.")
def compare_technologies(self, tech1, tech2):
return self.get_response(f"Compare {tech1} vs {tech2} in terms of features, performance, use cases, community support, and future prospects.")
def get_industry_trends(self):
return self.get_response("Describe current trends in software development and technology that are important for developers to be aware of.")
welcome_agent = WelcomeAgent()
project_agent = ProjectAgent()
career_agent = CareerAgent()
client_agent = ClientAgent()
research_agent = ResearchAgent()
@app.route('/static/images/default_avatar.png')
@app.route('/static/images/default_project.jpg')
def block_default_images():
response = app.make_response(
b'GIF89a\x01\x00\x01\x00\x80\x00\x00\xff\xff\xff\x00\x00\x00!\xf9\x04\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00,\x00\x00\x00\x00\x01\x00\x01\x00\x00\x02\x02D\x01\x00;')
response.headers['Content-Type'] = 'image/gif'
response.headers['Cache-Control'] = 'public, max-age=31536000'
response.headers['Expires'] = 'Thu, 31 Dec 2037 23:59:59 GMT'
return response
@app.route('/api/welcome', methods=['POST'])
def welcome_agent_endpoint():
data = request.json
message = data.get('message', '')
visitor_type = None
if 'employer' in message.lower():
visitor_type = 'employer'
elif 'client' in message.lower():
visitor_type = 'client'
elif 'programmer' in message.lower() or 'developer' in message.lower():
visitor_type = 'fellow_programmer'
if 'interest' in message.lower() or 'looking for' in message.lower():
interest = message.replace('interest', '').replace(
'looking for', '').strip()
response = welcome_agent.suggest_section(interest)
else:
response = welcome_agent.greet(visitor_type)
return jsonify({'response': response})
In this part of your codebase, you have more AI responses and a welcome API route.
Lastly, complete the code by adding this final piece at the end:
@app.route('/api/project', methods=['POST'])
def project_agent_endpoint():
data = request.json
message = data.get('message', '')
project_id = None
if 'e-commerce' in message.lower() or 'ecommerce' in message.lower():
project_id = 'project1'
elif 'task' in message.lower() or 'management' in message.lower():
project_id = 'project2'
elif 'data' in message.lower() or 'visualization' in message.lower() or 'dashboard' in message.lower():
project_id = 'project3'
if project_id and ('tell me more' in message.lower() or 'details' in message.lower()):
response = project_agent.get_project_details(project_id)
elif 'list' in message.lower() or 'all projects' in message.lower():
response = project_agent.get_project_list()
elif project_id:
response = project_agent.answer_technical_question(project_id, message)
else:
response = project_agent.get_response(
f"The user asked: '{message}'. Respond as if you are a project specialist for a portfolio website. "
"If they're asking about a specific project, suggest they mention one of the projects: "
"E-commerce Platform, Task Management App, or Data Visualization Dashboard."
)
return jsonify({'response': response})
@app.route('/api/career', methods=['POST'])
def career_agent_endpoint():
data = request.json
message = data.get('message', '')
if 'skills' in message.lower():
response = career_agent.get_skills_summary()
elif 'experience' in message.lower() or 'work history' in message.lower():
response = career_agent.get_experience_summary()
elif 'job' in message.lower() or 'position' in message.lower() or 'role' in message.lower():
response = career_agent.assess_job_fit(message)
else:
response = career_agent.get_response(
f"The user asked: '{message}'. Respond as if you are a career specialist for a portfolio website. "
"Suggest they ask about skills, experience, or job fit assessment."
)
return jsonify({'response': response})
@app.route('/api/client', methods=['POST'])
def client_agent_endpoint():
data = request.json
message = data.get('message', '')
if 'services' in message.lower() or 'offerings' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.get_services_overview()
elif 'web' in message.lower() and 'development' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.get_service_details('web_development')
elif 'mobile' in message.lower() and 'development' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.get_service_details('mobile_development')
elif 'consulting' in message.lower() or 'technical consulting' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.get_service_details('consulting')
elif 'process' in message.lower() or 'how does it work' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.explain_process()
elif 'proposal' in message.lower() or 'quote' in message.lower() or 'estimate' in message.lower():
response = client_agent.generate_proposal(message)
else:
response = client_agent.get_response(
f"The user asked: '{message}'. Respond as if you are a client specialist for a portfolio website. "
"Suggest they ask about services, the client engagement process, or request a proposal."
)
return jsonify({'response': response})
@app.route('/api/research', methods=['POST'])
def research_agent_endpoint():
data = request.json
message = data.get('message', '')
if 'compare' in message.lower() and ('vs' in message.lower() or 'versus' in message.lower()):
tech_parts = message.lower().replace('compare', '').replace(
'vs', ' ').replace('versus', ' ').split()
tech1 = tech_parts[0] if len(tech_parts) > 0 else ''
tech2 = tech_parts[-1] if len(tech_parts) > 1 else ''
response = research_agent.compare_technologies(tech1, tech2)
elif 'trends' in message.lower() or 'industry' in message.lower():
response = research_agent.get_industry_trends()
else:
response = research_agent.search_web(message)
return jsonify({'response': response})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.config['SEND_FILE_MAX_AGE_DEFAULT'] = 0
app.config['TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD'] = True # Ensure templates reload
@app.after_request
def add_header(response):
response.headers['Cache-Control'] = 'no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, max-age=0'
response.headers['Pragma'] = 'no-cache'
response.headers['Expires'] = '0'
return response
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5001, debug=True,
use_reloader=False, threaded=True)
Okay, if your file has errors, they're probably caused by the Python indentation. Hopefully, the formatting will not make them too difficult to fix.
The file is now complete, and you’ve created the rest of your AI API routes.
Running Our Python Backend
All that's left is to run your Flask server and get the backend up and running. You can do that with this run script inside the venv folder:
python3 main.py
Your backend should now be running on http://127.0.0.1:5001/. If you go to the page you will see an error like this:
Not Found
The requested URL was not found on the server. If you entered the URL manually please check your spelling and try again.
This is expected, because if you have checked the codebase, you’ll realise that there are no GET routes, only POST routes. To see them working, you need to use an HTTP client like Postman. Another option is to create some curl commands that send a POST request, which you can run from your terminal. Let's use curl because there is less setup. You’ll need to copy and paste the commands.
Each POST request will use exactly one API call on Groq Cloud for your API Key which you can view here https://console.groq.com/keys. Remember that it’s free to use but there are usage limits which you can read about in their documentation on Rate Limits.
I have provided some sample curl commands below - just copy and paste them into your terminal and hit enter, and you should see the response message:
1. Testing the Welcome Agent Endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5001/api/welcome \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "I am an employer looking for a skilled developer"}'
2. Testing the Project Agent Endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5001/api/project \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "Tell me more about the e-commerce project"}'
3. Testing the Career Agent Endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5001/api/career \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "What skills do you have?"}'
4. Testing the Client Agent Endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5001/api/client \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "What services do you offer?"}'
5. Testing the Research Agent Endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5001/api/research \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "What are the current trends in web development?"}'