
Chapter 6: Optimizing Soil Moisture and Quality with AI Models
Chapter 6: Optimizing Soil Moisture and Quality with AI Models 관련
The Importance of Soil Moisture Management
Effective soil moisture management is fundamental for optimizing crop yields, a goal that resonates universally within the agricultural sector. Inadequate or excessive moisture levels can lead to various complications like root diseases, nutrient leaching, and even yield reduction.
As AI-integrated farming techniques become more sophisticated, they offer a seamless solution to these age-old problems. By employing AI models, farmers can ensure crops consistently receive just the right amount of water.
A powerful aspect of these AI models is their ability to monitor and interpret various data points in real-time, providing insights that would be impossible through manual methods. For instance, imagine a system that analyzes weather forecasts, soil types, and plant needs daily, adjusting irrigation schedules to match this dynamic environment precisely. It's like having a digital agronomist tirelessly working to keep your soil in perfect condition. This heightened level of precision translates directly to higher yields and better crop health.
Not only does this help issue-specific concerns like drought or over-irrigation, but it also integrates seamlessly into larger farm management systems. By identifying optimal times for water distribution, AI allows for more strategic planning and resource allocation. Think of it as a cycle: healthier soil leads to healthier crops, requiring even less intervention. Thus, the benefits cascade, leading to more efficient and sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of AI in Optimizing Soil Quality
One of the most compelling advantages of using artificial intelligence in soil quality optimization is its precision. Traditional farming often relies on blanket treatments—broadly applying water or fertilizer across entire fields. AI transforms this into a surgical procedure, tailored to the specific needs of different soil segments.
For example, a farmer might employ an AI model to identify that a particular section of a field is nutrient-deficient. Rather than fertilizing the entire field, resources can be directed precisely where they are needed most.
Predictive analytics represent another revolutionary facet of AI, eliminating the guesswork from farming. By analyzing a rich history of data—soil tests, weather conditions, crop performance—AI enables farmers to anticipate future conditions and prepare accordingly. This kind of foresight can be invaluable when planning crop rotations, anticipating pest invasions, or deciding on the optimal planting and harvesting times. Imagine having a crystal ball that tells you exactly when to plant each year, aligning perfectly with the best-growing conditions.
The key takeaway here is that AI can help provide sustainable solutions. As AI models become more sophisticated, their ability to adapt to changing climates and soil conditions grows, providing a robust platform for future farming endeavors. In this way, AI-enabled soil quality management systems are contributing towards global food security, a critical need underscored in discussions on agricultural advancements.
Integration with Existing Farming Practices
The integration of AI into existing farming practices should be seamless, enhancing rather than disrupting daily operations. Many farmers may be wary of adopting new technologies, fearing complexity or disruption. But today's AI systems are designed for usability. They often integrate directly with existing farm management software, providing a unified interface for all your agricultural needs. For example, systems like John Deere's Operations Center offer modules that incorporate AI-driven insights into traditional farm management tools.
Farmers can see real-time data on soil moisture levels, nutrient content, and irrigation needs, all in one place. These platforms often offer mobile applications, allowing farmers to access this critical information from anywhere, making decisions on-the-go. The ease of use and accessibility of AI models demystify the technology, making it more approachable. It's not about replacing the farmer's expertise but augmenting it—providing tools that enable smarter, more efficient farming.
Full integration into irrigation systems means the AI can automatically adjust water levels without manual intervention. This automation ensures that even the minutest changes in soil conditions are addressed immediately, maintaining optimal growing conditions at all times. Think of it as a smart home system but for your crops—a digital assistant that ensures everything runs smoothly, even when you cannot be present.
Balancing Technological Advancements and Practical Applications
While the promise of AI in optimizing soil moisture and quality is enormous, its practical application requires a balanced approach. Not all farms are the same, and the variance in soil types, climate conditions, and crop types means a one-size-fits-all solution isn’t feasible.
Tailoring AI models to fit specific needs is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness. Customizable AI platforms are gaining traction because they allow for this level of specificity.
Take, for instance, a farm situated in a semi-arid region. The soil here typically has lower organic content and higher salinity levels. An AI model geared towards this specific environment will focus on conserving water while improving soil quality through targeted fertilization techniques and organic amendments.
Contrast this with a farm in a temperate climate, where the AI might prioritize managing periodic heavy rains to prevent soil erosion and nutrient loss. The customization of AI applications ensures that solutions are relevant and effective, driving meaningful improvements in any farming context.
The interdisciplinary nature of AI-powered farming highlights the need for collaboration between technology developers, agronomists, and the farmers themselves. Each stakeholder brings invaluable expertise, and their combined efforts can overcome any initial hurdles.
Training programs and workshops can further this integration, empowering farmers to use these technologies effectively. Enhancing the farmers' understanding of how these tools work allows them to make more informed decisions, unlocking the full potential of AI in agriculture.
Addressing Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any technological advancement, the implementation of AI in soil moisture and quality management comes with its own set of challenges. One significant concern is data privacy. Farms collect vast amounts of data—weather conditions, soil properties, crop performance—that is valuable not just to farmers but to numerous stakeholders, including corporations and governments. Ensuring this data is used ethically and remains secure is paramount.
Another challenge is accessibility. While larger, well-funded farms can afford to implement advanced AI systems, smaller farms often operate on tighter budgets. Ensuring equitable access to this transformative technology is crucial for its widespread adoption. Public funding, subsidies, and collaborative efforts between private sectors and government bodies can create pathways for smaller farms to benefit from AI advancements.
While AI systems can alleviate many manual tasks, reliance on technology should not come at the expense of traditional farming knowledge. The wisdom and experience of seasoned farmers offer insights that cannot be wholly replicated by algorithms. Thus, a balanced approach that combines the best of both worlds—traditional agriculture knowledge and modern AI capabilities—will yield the most robust, sustainable farming practices.
Towards Sustainable and Resilient Agriculture
The future of agriculture lies in leveraging technological advancements like AI to create systems that are not only high-yielding but also sustainable and resilient. AI-powered soil moisture and quality management systems offer a glimpse into this future, where data-driven decisions replace guesswork, and precise interventions lead to optimal outcomes. The cascading benefits—from increased crop yields and reduced resource use to enhanced food security—highlight the immense potential of this approach.
The adoption of these AI models is an essential step towards realizing the goals set out in AI in Agriculture: How AI-Enhanced Farming Could Increase Crop Yields by 70% by 2030. With every farm that integrates AI technology, we get closer to a world where agricultural practices are sustainable, efficient, and resilient to the challenges posed by climate change and growing populations.
Code Examples
Below are advanced examples of how Large Language Models (LLMs) can be incorporated into AI models for optimizing soil moisture and quality management in agriculture. These examples align well with the ones from the chapter on optimizing soil moisture and quality.
Example 1: AI-driven real-time soil moisture management
Objective: Use an LLM to dynamically adjust irrigation schedules based on soil moisture sensor data, weather forecasts, and crop needs. The system optimizes water distribution in real-time, considering potential root diseases and nutrient leaching.
import openai
from datetime import datetime
# Sample input data from real-time sensors and weather forecasts
soil_data = {
"moisture_level": 40, # Soil moisture percentage
"root_zone_temperature": 25, # Temperature in Celsius
"potential_root_disease_risk": "moderate"
}
weather_forecast = {
"today": {"temp": 30, "humidity": 60, "precipitation": 5}, # °C, %, mm
"tomorrow": {"temp": 32, "precipitation": 10} # °C, mm
}
crop_needs = {
"growth_stage": "flowering",
"water_requirement": "high"
}
# Describe the current data to the LLM
data_description = (
f"The current soil moisture level is {soil_data['moisture_level']}%. "
f"Root zone temperature is {soil_data['root_zone_temperature']}°C. "
f"There is a {soil_data['potential_root_disease_risk']} risk of root disease. "
f"Today's weather forecast shows a temperature of {weather_forecast['today']['temp']}°C "
f"with 5mm of precipitation and 60% humidity. The crop is in the flowering stage, "
f"and its water requirement is high."
)
# Use an LLM to adjust the irrigation schedule based on real-time data
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI expert specializing in soil moisture management and irrigation."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the following data, provide an optimized irrigation schedule: {data_description}"}
]
)
irrigation_schedule = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(irrigation_schedule)
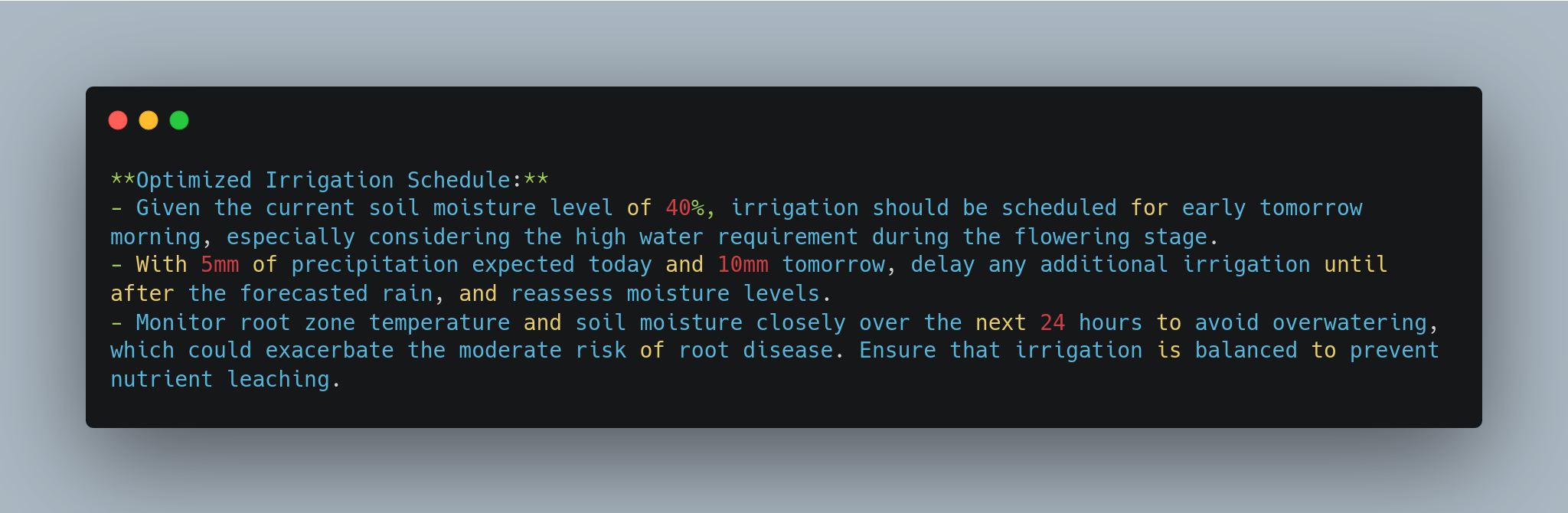
**Optimized Irrigation Schedule:**
- Given the current soil moisture level of 40%, irrigation should be scheduled for early tomorrow morning, especially considering the high water requirement during the flowering stage.
- With 5mm of precipitation expected today and 10mm tomorrow, delay any additional irrigation until after the forecasted rain, and reassess moisture levels.
- Monitor root zone temperature and soil moisture closely over the next 24 hours to avoid overwatering, which could exacerbate the moderate risk of root disease. Ensure that irrigation is balanced to prevent nutrient leaching.
lunartech.ai
Example 2: AI-enhanced soil quality analysis and fertilization strategy
Objective: Use an LLM to analyze soil quality based on nutrient levels and crop requirements. The system recommends precise fertilization strategies based on real-time and historical data, helping avoid over-fertilization and nutrient leaching.
import openai
# Sample input data from soil tests and crop requirements
soil_data = {
"pH": 6.5,
"nutrient_levels": {"nitrogen": 30, "phosphorus": 15, "potassium": 25}, # ppm
"organic_matter": 3.0 # percentage
}
crop_data = {
"crop_type": "wheat",
"growth_stage": "early vegetative",
"nutrient_requirement": {"nitrogen": "high", "phosphorus": "moderate", "potassium": "low"}
}
# Generate description for the LLM based on the input data
data_description = (
f"The soil pH is {soil_data['pH']}, and the nutrient levels are nitrogen at {soil_data['nutrient_levels']['nitrogen']} ppm, "
f"phosphorus at {soil_data['nutrient_levels']['phosphorus']} ppm, and potassium at {soil_data['nutrient_levels']['potassium']} ppm. "
f"The organic matter content is {soil_data['organic_matter']}%. The crop type is wheat, which is in the early vegetative stage and has high nitrogen requirements."
)
# Use LLM to generate a precise fertilization strategy
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI agronomist specializing in soil quality and fertilization."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the following soil and crop data, provide a fertilization strategy: {data_description}"}
]
)
fertilization_strategy = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(fertilization_strategy)
lunartech.ai
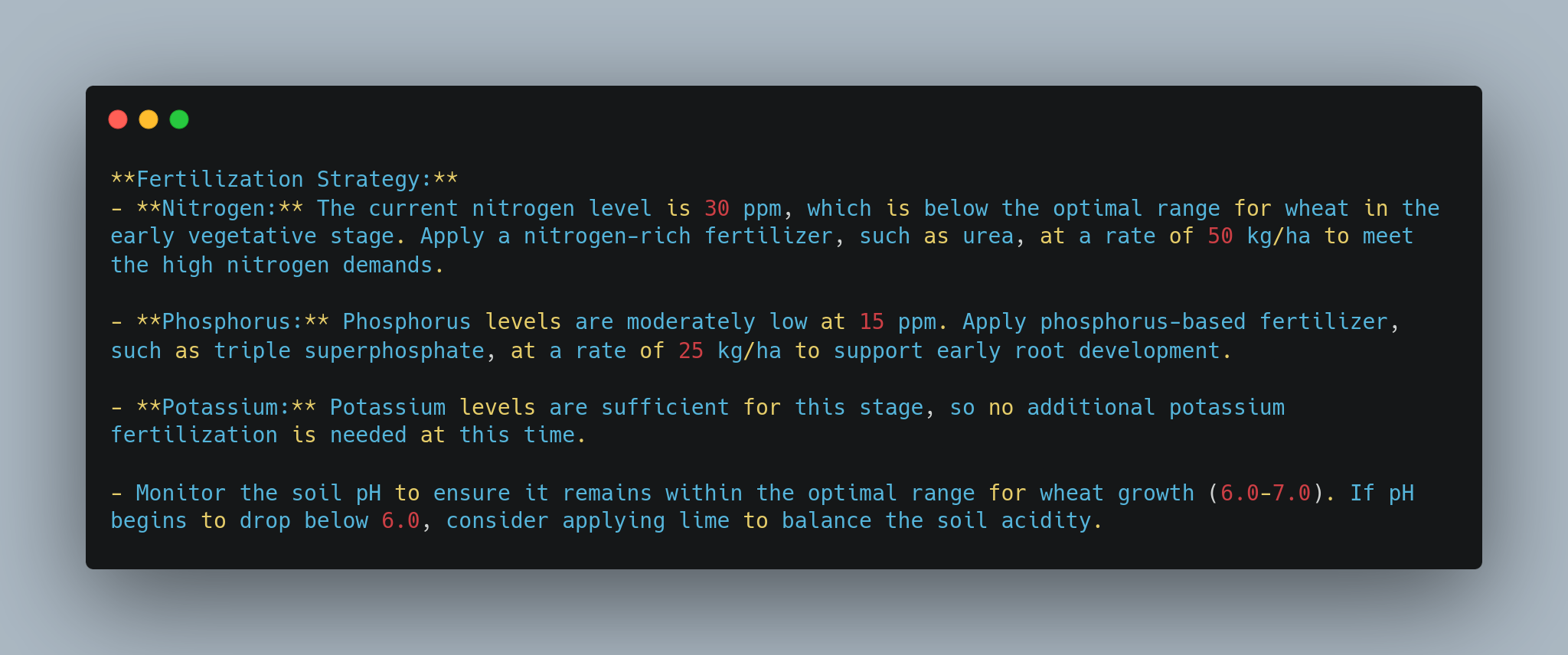
**Fertilization Strategy:**
- **Nitrogen:** The current nitrogen level is 30 ppm, which is below the optimal range for wheat in the early vegetative stage. Apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer, such as urea, at a rate of 50 kg/ha to meet the high nitrogen demands.
- **Phosphorus:** Phosphorus levels are moderately low at 15 ppm. Apply phosphorus-based fertilizer, such as triple superphosphate, at a rate of 25 kg/ha to support early root development.
- **Potassium:** Potassium levels are sufficient for this stage, so no additional potassium fertilization is needed at this time.
- Monitor the soil pH to ensure it remains within the optimal range for wheat growth (6.0-7.0). If pH begins to drop below 6.0, consider applying lime to balance the soil acidity.
lunartech.ai
Example 3: AI-powered predictive analytics for soil moisture and quality optimization
Objective: Use an LLM to combine predictive analytics and historical data to forecast future soil moisture conditions, nutrient levels, and irrigation needs. The AI provides a long-term soil management strategy based on weather predictions and crop growth stages.
import openai
from datetime import datetime
# Historical and predictive input data for AI analysis
historical_data = {
"soil_moisture_trend": [40, 35, 30, 25], # % moisture over past 4 weeks
"nutrient_depletion": {"nitrogen": 2, "phosphorus": 1, "potassium": 0.5}, # ppm depletion rate per week
"weather_trends": [
{"week": 1, "precipitation": 20}, # mm of rain
{"week": 2, "precipitation": 10},
{"week": 3, "precipitation": 0},
{"week": 4, "precipitation": 5}
]
}
current_conditions = {
"soil_moisture": 30, # current soil moisture percentage
"weather_forecast": {"next_week_precipitation": 15}, # mm of expected rain
"growth_stage": "mid-vegetative"
}
# Generate description for the LLM
data_description = (
f"Over the past 4 weeks, soil moisture has decreased from 40% to 25%. Nitrogen has been depleting at a rate of 2 ppm per week. "
f"The precipitation levels have been fluctuating, with only 5mm last week and 15mm expected next week. "
f"The crop is currently in the mid-vegetative stage."
)
# Use LLM to provide long-term soil moisture and quality optimization strategy
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI agronomist specializing in predictive analytics for soil moisture and quality."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the following historical and predictive data, provide a soil moisture and quality management strategy: {data_description}"}
]
)
soil_management_strategy = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(soil_management_strategy)
lunartech.ai
**Soil Moisture and Quality Management Strategy**
Based on the historical data and current conditions, the following strategy is recommended to optimize soil moisture and maintain soil quality:
1. **Irrigation Management**
- **Scheduled Irrigation:** Implement a drip irrigation system to provide consistent moisture levels, targeting a soil moisture percentage between 30% and 35%. This helps compensate for the recent decline from 40% to 25%.
- **Rainfall Utilization:** With an expected 15mm of precipitation next week, adjust the irrigation schedule to reduce water input accordingly, preventing waterlogging and conserving water resources.
2. **Nutrient Management**
- **Nitrogen Supplementation:** Given the depletion rate of 2 ppm per week, apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer bi-weekly to replenish soil nitrogen levels and support plant growth during the mid-vegetative stage.
- **Phosphorus and Potassium Maintenance:** Continue monitoring phosphorus and potassium levels, applying supplements as needed to maintain balanced nutrient availability.
3. **Soil Conservation Practices**
- **Mulching:** Apply organic mulch around crops to reduce soil evaporation, maintain moisture levels, and improve soil structure.
- **Cover Cropping:** Introduce cover crops during off-seasons to enhance soil organic matter, prevent erosion, and improve nutrient retention.
4. **Weather Adaptation**
- **Drainage Management:** Ensure proper drainage systems are in place to handle the variability in precipitation, especially during weeks with low rainfall.
- **Weather Monitoring:** Utilize weather forecasting tools to make informed decisions on irrigation and nutrient application, adapting strategies based on real-time data.
5. **Crop Management**
- **Growth Stage Optimization:** During the mid-vegetative stage, focus on practices that support robust leaf and stem development, ensuring that soil conditions do not limit plant growth.
- **Pest and Disease Monitoring:** Regularly inspect crops for signs of stress, pests, or diseases that may arise from fluctuating soil moisture and nutrient levels.
6. **Long-Term Soil Health**
- **Soil Testing:** Conduct quarterly soil tests to monitor nutrient levels, pH, and organic matter content, allowing for data-driven adjustments to management practices.
- **Sustainable Practices:** Invest in sustainable farming practices such as crop rotation and reduced tillage to enhance soil health and resilience against environmental stressors.
7. **Technology Integration**
- **Soil Moisture Sensors:** Deploy soil moisture sensors to obtain real-time data, enabling precise irrigation control and timely interventions.
- **Data Analytics:** Utilize data analytics platforms to track historical trends and predict future soil moisture and nutrient needs, optimizing resource allocation.
**Implementation Timeline:**
- **Immediate (Next 1-2 Weeks):**
- Install or calibrate drip irrigation systems.
- Apply nitrogen-based fertilizers.
- Begin mulching around crop areas.
- **Short-Term (Next 1-3 Months):**
- Monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels weekly.
- Adjust irrigation schedules based on rainfall and sensor data.
- Introduce cover crops during off-seasons.
- **Long-Term (6 Months - 1 Year):**
- Conduct comprehensive soil health assessments.
- Implement sustainable farming practices.
- Invest in advanced soil monitoring technologies.
By following this strategy, you can effectively manage soil moisture levels, replenish essential nutrients, and maintain overall soil health, leading to sustained crop productivity and resilience against environmental challenges.