
Chapter 3: Labor Optimization Solutions Through AI in Agriculture
Chapter 3: Labor Optimization Solutions Through AI in Agriculture 관련
Agricultural enterprises worldwide are increasingly leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) to address one of the most pressing challenges: labor shortages. AI technologies offer transformative solutions that enhance efficiency and optimize various operations within the sector.
By examining AI's role in enhancing farm labor management, precision agriculture, and AI-driven robotics and automation, we can appreciate its profound impact on overcoming workforce scarcity.
Enhanced Farm Labor Management
Farm labor management has traditionally been resource-intensive, often hindered by inefficiencies resulting from manual planning and unpredictable variables like weather.
AI models integrated into farm management software revolutionize this space by enabling highly precise resource allocation and task assignment. Machine learning algorithms analyze extensive datasets encompassing soil conditions, weather patterns, crop growth stages, and historical farm performance to devise actionable insights.
For example, AI can identify the optimal times for planting, irrigating, and harvesting by processing current and forecasting data. This predictive capability ensures farming activities are synchronized with peak resource availability, minimizing labor bottlenecks. This means that farms can plan their workforce requirements more effectively, reducing downtime and enhancing overall productivity.
But AI's potential extends beyond mere task scheduling. It supports decision-making processes through real-time feedback mechanisms, allowing farm managers to adjust strategies dynamically. For instance, if an unexpected weather change is detected, AI can prompt adjustments to irrigation schedules or suggest protective measures, thereby safeguarding crops and ensuring labor is utilized efficiently.
Let’s look at an example of how you’d put this into practice.
Objective: Utilize an LLM to generate dynamic task scheduling for farm labor management based on weather, soil, and crop growth data. The system adapts in real-time to changing environmental conditions.
import openai
import datetime
# Sample environmental data (weather, soil moisture, crop growth)
environmental_data = {
"weather_forecast": {
"today": {"temp": 28, "precipitation": 20, "wind_speed": 10},
"tomorrow": {"temp": 30, "precipitation": 50, "wind_speed": 5}
},
"soil_conditions": {
"moisture_level": 60, # percentage
"fertility_level": "high"
},
"crop_stage": "vegetative"
}
# Convert environmental data into a readable description
environment_description = (
f"Today's weather forecast: temperature {environmental_data['weather_forecast']['today']['temp']}°C, "
f"precipitation {environmental_data['weather_forecast']['today']['precipitation']}mm, wind speed {environmental_data['weather_forecast']['today']['wind_speed']} km/h. "
f"Soil moisture level is {environmental_data['soil_conditions']['moisture_level']}% and fertility level is {environmental_data['soil_conditions']['fertility_level']}. "
f"The crop is currently in the {environmental_data['crop_stage']} stage."
)
# Use LLM to generate a farm labor schedule based on environmental conditions
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an expert in farm labor management using AI."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Given the following environmental data, provide a dynamic labor schedule for planting, irrigation, and harvesting: {environment_description}"}
]
)
labor_schedule = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(labor_schedule)
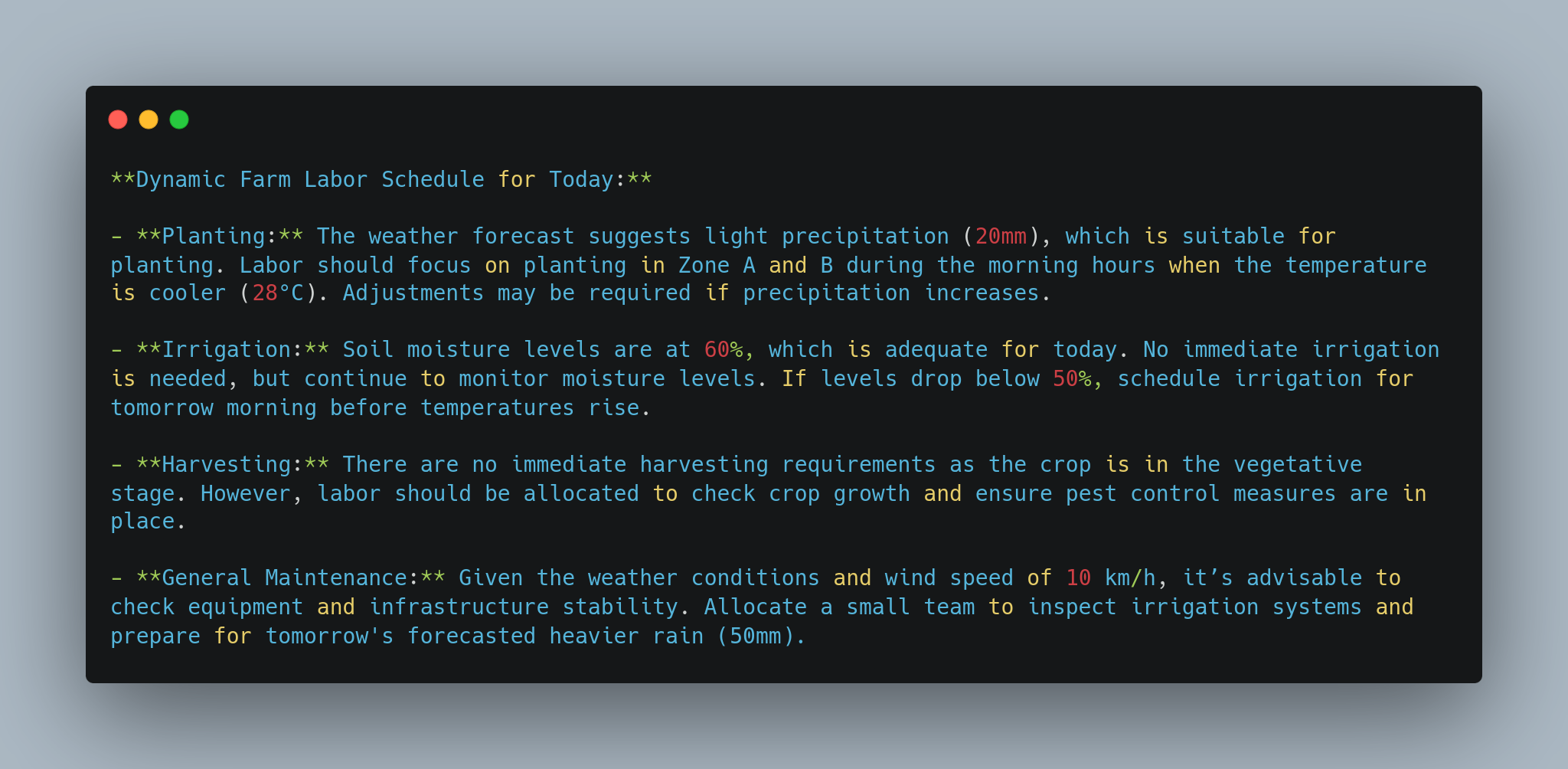
**Dynamic Farm Labor Schedule for Today:**
- **Planting:** The weather forecast suggests light precipitation (20mm), which is suitable for planting. Labor should focus on planting in Zone A and B during the morning hours when the temperature is cooler (28°C). Adjustments may be required if precipitation increases.
- **Irrigation:** Soil moisture levels are at 60%, which is adequate for today. No immediate irrigation is needed, but continue to monitor moisture levels. If levels drop below 50%, schedule irrigation for tomorrow morning before temperatures rise.
- **Harvesting:** There are no immediate harvesting requirements as the crop is in the vegetative stage. However, labor should be allocated to check crop growth and ensure pest control measures are in place.
- **General Maintenance:** Given the weather conditions and wind speed of 10 km/h, it’s advisable to check equipment and infrastructure stability. Allocate a small team to inspect irrigation systems and prepare for tomorrow's forecasted heavier rain (50mm).
lunartech.ai
This example focused on enhancing farm labor management by dynamically generating a labor schedule for farming tasks (for example, planting, irrigation, harvesting) based on real-time environmental data such as weather, soil conditions, and crop growth stages. The LLM ensured that the labor schedule adapted to changing conditions.
Precision Agriculture for Labor Optimization
Precision agriculture exemplifies the integration of AI and predictive analytics to optimize labor usage. This approach tailors farming practices to the specific needs of different field zones by analyzing real-time data on soil moisture levels, crop health, and weather conditions. Integrating AI into precision agriculture amplifies its effectiveness.
Imagine a farmer managing a vast field with varying soil types and fertility levels. Traditionally, uniform treatment would have been applied across the entire field, leading to inefficiencies and potential wastage of resources.
But AI can create detailed field maps, segmenting the land into manageable zones, each with tailored treatment plans. This ensures that labor-intensive tasks such as fertilization and pest control are precisely directed where needed, maximizing their impact and conserving resources.
AI's real-time data processing capabilities also enable predictive maintenance of equipment. By continuously monitoring machinery and identifying signs of wear or potential failure, AI-driven systems can schedule preemptive repairs, preventing costly downtime and labor disruptions. This predictive maintenance significantly enhances operational efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of equipment, leading to long-term cost savings.
Now let’s see an example of how you could use precision agriculture with LLMs to optimize labor and resources:
Objective: Integrate an LLM to analyze real-time precision agriculture data and provide recommendations for labor allocation in specific zones based on soil moisture, crop health, and machine maintenance needs.
import openai
# Sample precision agriculture data for a large field
precision_ag_data = {
"zones": {
"Zone_1": {"soil_moisture": 40, "crop_health": "good", "fertilization_need": "low"},
"Zone_2": {"soil_moisture": 30, "crop_health": "moderate", "fertilization_need": "high"},
"Zone_3": {"soil_moisture": 25, "crop_health": "poor", "fertilization_need": "high"}
},
"machinery_status": {
"tractor_1": {"status": "operational", "maintenance_due_in_days": 5},
"tractor_2": {"status": "requires_maintenance", "maintenance_due_in_days": 0}
}
}
# Convert precision agriculture data into a readable description
agriculture_description = (
f"Zone 1 has soil moisture at 40%, crop health is good, and low fertilization is needed. "
f"Zone 2 has soil moisture at 30%, crop health is moderate, and high fertilization is needed. "
f"Zone 3 has soil moisture at 25%, crop health is poor, and high fertilization is needed. "
f"Tractor 1 is operational and requires maintenance in 5 days. Tractor 2 requires immediate maintenance."
)
# Use LLM to generate labor allocation recommendations
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI expert specializing in precision agriculture labor optimization."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the following precision agriculture data, provide labor recommendations for today: {agriculture_description}"}
]
)
labor_recommendations = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(labor_recommendations)
lunartech.ai
**Labor Allocation Recommendations for Today:**
- **Zone 1:** Since soil moisture is at 40% and crop health is good, allocate minimal labor for fertilization here. Focus on general crop monitoring, with labor redirected to other zones.
- **Zone 2:** This zone requires more attention due to moderate crop health and lower soil moisture (30%). Allocate a team for high-level fertilization tasks and schedule irrigation in the afternoon when temperatures are lower. Ensure laborers monitor soil moisture to avoid overwatering.
- **Zone 3:** Given the poor crop health and low soil moisture (25%), prioritize labor here. Allocate labor for both high-level fertilization and immediate irrigation. Additionally, plan a follow-up visit to assess crop recovery within 48 hours.
- **Machinery:** Tractor 2 requires immediate maintenance and should not be used today. Tractor 1 is operational but will require maintenance in the coming days. Assign a small maintenance crew to inspect Tractor 1 and prepare it for upcoming tasks.
These labor recommendations will help optimize workforce distribution while ensuring efficient resource use and timely crop interventions.
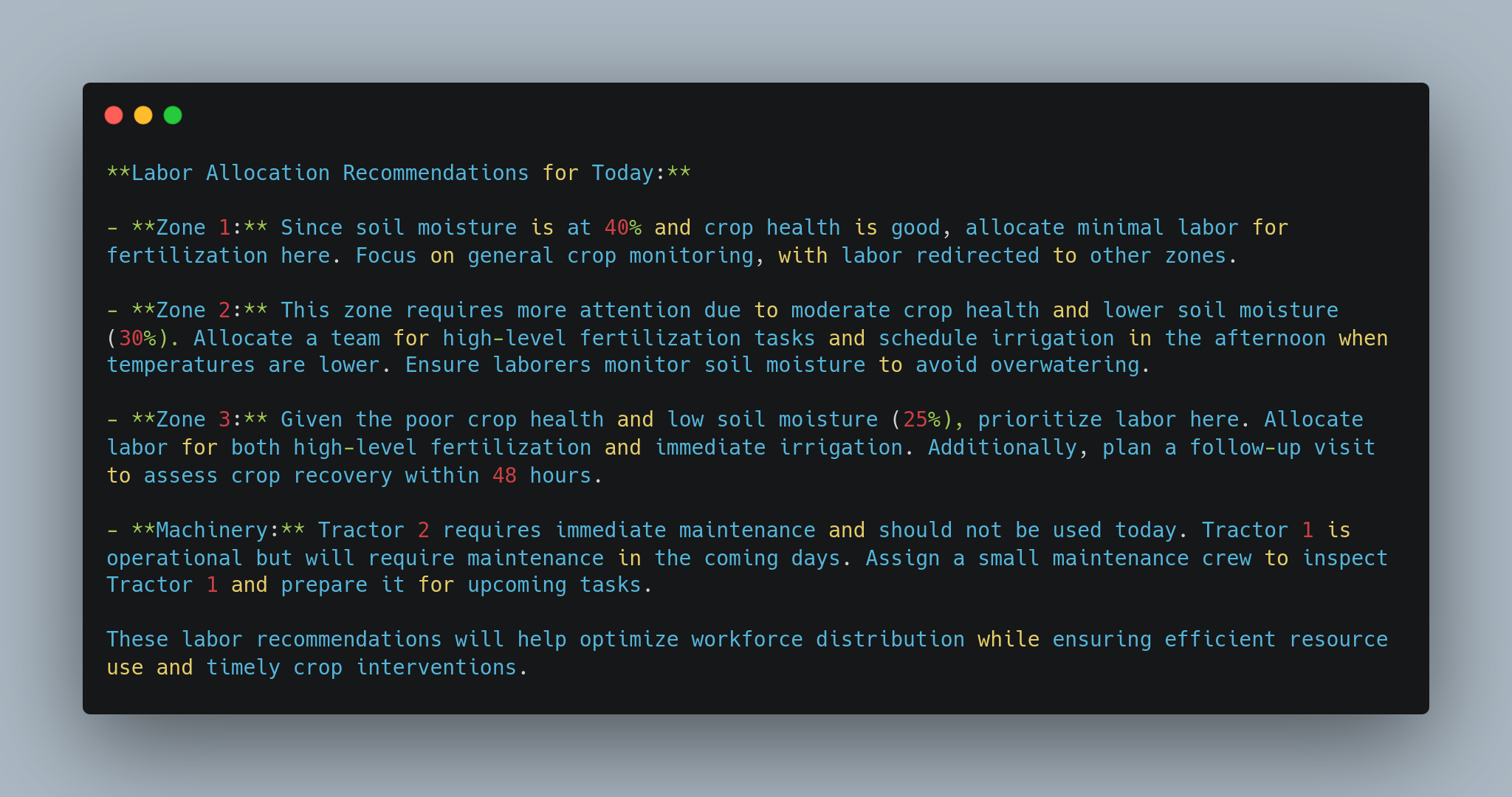
In this example, you saw how you can use precision agriculture with LLMs to analyze zone-specific data (soil moisture, crop health) and provide optimized labor allocation recommendations. It also considered machinery maintenance requirements to prevent downtime.
AI-Driven Robotics and Automation
One of the most profound applications of AI in agriculture is in robotics and automation. AI-driven robots are designed to perform tasks traditionally requiring manual labor, such as planting, harvesting, and sorting. These robots are not only faster and more accurate but also capable of operating in conditions that might be challenging for human workers.
Take autonomous tractors, for instance. These vehicles use AI to navigate fields, planting seeds with pinpoint accuracy. They can work tirelessly, undeterred by fatigue or harsh weather, resulting in more consistent and higher-quality planting.
Similarly, harvesting robots equipped with advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms can distinguish between ripe and unripe fruits, ensuring optimal harvest times and reducing wastage.
Robotic process automation extends to post-harvest activities as well. Automated systems for sorting and packaging crops enhance the speed and accuracy of these labor-intensive tasks. These robots can be trained to recognize various crop qualities, ensuring only the best produce reaches the market.
AI-driven robotics can also adapt to various environmental conditions and crop varieties. This adaptability ensures that farms employing AI technologies enjoy consistent performance regardless of changes in soil types or weather patterns, overcoming one of the significant limitations of traditional farming methods.
Sustainable Farming Practices
The integration of AI technologies in agriculture also paves the way for sustainable farming practices. By optimizing resource utilization and minimizing wastage, AI helps in reducing the environmental footprint of agricultural activities. For instance, precision irrigation systems using AI algorithms ensure water is used efficiently, addressing sustainability concerns in water-scarce regions.
Furthermore, AI can assist in monitoring and managing the health of crops with minimal chemical inputs. Machine learning algorithms can analyze data from sensors and detect signs of diseases or pest attacks early, allowing for targeted intervention with minimal pesticide use. This approach not only ensures healthier crops but also contributes to better environmental and consumer health.
Now you have a better idea about how AI can work to address the persistent issue of labor shortages in agriculture. By enhancing farm labor management, enabling precision agriculture, and driving robotics and automation, AI technologies significantly boost operational efficiency and productivity. These innovations ensure that farmers can manage their resources more effectively, maintain sustainable practices, and ultimately achieve higher crop yields.