
Chapter 7: Sustainable Land Use Strategies with Agricultural Technology
Chapter 7: Sustainable Land Use Strategies with Agricultural Technology 관련
In the landscape of modern agriculture, the promise of AI-enhanced farming sets a compelling context for exploring sustainable land use strategies supported by technological advancements.
The confluence of artificial intelligence and sustainable agricultural practices not only addresses the need for increased productivity but also emphasizes the importance of environmental stewardship.
This chapter delves into how the integration of AI and other cutting-edge technologies can revolutionize land use, optimizing resource management while promoting ecological balance.
Precision Agriculture for Resource Optimization
Precision agriculture, a hallmark of modern farming, leverages AI models and predictive analytics to refine agricultural practices at an unprecedented scale. By employing advanced data analytics, farmers can monitor vital parameters such as soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health with pinpoint accuracy.
For example, soil moisture sensors connected to AI platforms can provide real-time data, enabling farmers to optimize irrigation schedules to conserve water without compromising crop health.
This level of precision empowers farmers to tailor their use of fertilizers and pesticides, reducing waste and enhancing soil quality. AI-driven soil quality assessments can guide the application of nutrients specifically where they are needed, rather than blanket coverage, which can lead to pollution and soil degradation. By focusing on data-driven decisions, precision agriculture not only enhances yield but also aligns farming practices with sustainable land management.
AI-Powered Farm Management Software
AI-powered farm management software represents the next frontier in agricultural efficiency. These platforms offer comprehensive tools to streamline farm operations, from resource allocation to day-to-day task management. The integration of computer vision technology allows for early detection of crop anomalies, such as nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations, through the analysis of high-resolution images.
This proactive approach can significantly mitigate crop losses and minimize the need for chemical interventions, thus fostering more sustainable farming practices. Moreover, robotic process automation (RPA) addresses labor shortages by automating routine tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting. This not only reduces operational strain but also enables farmers to focus on strategic decision-making and long-term planning.
Sustainable Practices for Enhanced Yields
Sustainable agricultural practices supported by AI technologies embrace the dual goals of maximizing productivity and minimizing environmental impact. AI-powered precision irrigation systems, for example, use weather forecasts and soil moisture data to deliver water only when and where it is needed. This not only conserves water but also ensures that crops receive optimal hydration for maximum growth.
Also, the adoption of AI solutions for sustainable land use often comes with financial incentives. Governments and international bodies increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable farming and offer subsidies or grants to farmers who implement eco-friendly technologies. These incentives not only offset the initial cost of adopting new technologies but also promote long-term benefits such as improved soil health, reduced pollution, and enhanced biodiversity.
Embracing the Future of Agriculture with AI
The future of agriculture lies in the seamless integration of AI technologies, transforming traditional farming into a sophisticated, data-driven practice. By addressing critical challenges such as climate variability, labor shortages, and resource constraints, AI technologies ensure the resilience and sustainability of the global food system.
For example, machine learning algorithms can predict climate-related risks, allowing farmers to adapt their planting schedules and crop selections accordingly. This adaptive approach is essential in a world where climate change poses an increasing threat to food security. By leveraging AI, farmers can make informed decisions that not only enhance productivity but also safeguard the environment for future generations.
Optimizing Resource Management through Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture stands at the forefront of resource management optimization. Through the use of AI models and big data analytics, farmers can monitor and manage resources with precision, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and sustainability.
Soil moisture sensors are a prime example of technology enabling precise irrigation management. These sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, helping farmers determine the exact amount of water needed. This ensures optimal crop hydration, reduces water wastage, and prevents over-irrigation, which can lead to soil erosion and nutrient runoff.
Beyond irrigation, precision agriculture plays a vital role in managing soil quality. AI-powered tools analyze soil samples to assess nutrient levels and composition. Farmers can then tailor fertilizer application to the specific needs of different soil sections, avoiding overuse and minimizing environmental impact. This targeted approach not only enhances crop yield but also promotes soil health and reduces the risk of contamination in nearby water sources.
The integration of weather pattern analysis further enhances resource management. Predictive analytics can forecast weather conditions with high accuracy, allowing farmers to plan their activities accordingly. Whether it's adjusting planting schedules to avoid adverse weather or applying protective measures against frost or drought, precision agriculture empowers farmers to make informed decisions that optimize resource use.
Enhancing Farm Efficiency with AI Technologies
One of the most significant contributions of AI to agriculture is the development of advanced farm management software. These platforms leverage AI algorithms to streamline farm operations, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity. By tracking and managing resources such as labor, equipment, and inputs, these systems offer a holistic view of farm activities.
Computer vision technology, integrated into farm management software, provides farmers with invaluable insights into crop health. High-resolution images captured by drones or sensors undergo detailed analysis, enabling early detection of issues such as nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, or disease outbreaks. Timely intervention can prevent these problems from spreading and causing extensive damage. And AI-powered recommendation engines suggest appropriate remedial actions, empowering farmers to address issues effectively.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is another key component in enhancing farm efficiency. Automation of repetitive and labor-intensive tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting not only reduces the reliance on human labor but also ensures precision and consistency. This, in turn, leads to higher productivity and reduced operational costs.
Promoting Sustainable Farming Practices with AI
Sustainable land use practices are integral to achieving long-term agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impact. AI technologies play a pivotal role in promoting these practices by optimizing land use and conserving natural resources. Precision irrigation systems, powered by AI, exemplify the synergy between technology and sustainability. By delivering water precisely when and where it is needed, these systems reduce water wastage and ensure that crops receive optimal hydration.
AI-driven solutions for nutrient management also help contribute to sustainable farming by minimizing the use of chemical fertilizers. By analyzing soil nutrient levels, AI models recommend targeted fertilization, ensuring that nutrients are applied only where required. This not only enhances crop yield but also prevents over-fertilization, which can lead to soil and water pollution.
Fuel consumption is another significant area where AI can drive sustainability. Autonomous machinery equipped with AI algorithms optimizes fuel use by planning efficient routes and minimizing idle time. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions and lowers operational costs, contributing to both environmental and economic sustainability.
Financial Incentives for Sustainable Farming
The adoption of sustainable land use strategies is often facilitated by financial incentives provided by governments and organizations. These incentives encourage farmers to invest in AI-driven technologies that promote sustainability and long-term benefits. Subsidies, grants, and tax incentives help offset the initial costs of implementing new technologies, making them more accessible to farmers.
For instance, governments may offer subsidies for the installation of precision irrigation systems or provide grants for adopting AI-powered soil analysis tools. These financial incentives not only support the transition to sustainable farming practices but also recognize the broader societal benefits, such as improved water quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and enhanced biodiversity.
Sustainable farming practices driven by AI technologies can also lead to increased profitability for farmers. By optimizing resource use, reducing input costs, and enhancing crop yield, these practices contribute to higher economic returns. Farmers who embrace AI-driven solutions are better positioned to achieve long-term financial stability while contributing to a more sustainable food system.
Building a Resilient Future with AI in Agriculture
The integration of AI technologies in agriculture represents a paradigm shift that addresses critical challenges and paves the way for a resilient and sustainable future. By harnessing the power of AI, farmers can navigate the complexities of modern farming, optimize resource use, and mitigate environmental impact.
AI-driven predictive analytics empower farmers to adapt to changing climatic conditions. By analyzing historical weather data and current trends, AI models can predict future weather patterns with high precision. This enables farmers to make proactive decisions, such as adjusting planting schedules, selecting resilient crop varieties, and implementing protective measures. Such adaptive strategies are essential in the face of climate change, ensuring the continuity of agricultural productivity.
Labor shortages, a persistent challenge in agriculture, are effectively addressed by AI-powered automation. Robots and autonomous machinery perform labor-intensive tasks with precision and reliability, reducing the dependence on human labor. This not only increases operational efficiency but also allows farmers to focus on strategic planning and innovation.
Code Examples
Here are three advanced examples of how Large Language Models (LLMs) can be integrated into AI technologies to enhance Sustainable Land Use Strategies with Agricultural Technology:
Example 1: AI-driven precision agriculture for resource optimization
Objective: Use LLM to analyze data from soil sensors, satellite imagery, and weather forecasts to optimize irrigation and fertilizer use while maintaining sustainability. This example will help farmers optimize resource use, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainable land management.
import openai
# Sample input data from soil sensors, satellite imagery, and weather forecasts
farm_data = {
"soil_moisture": {
"zone_A": 45, # percentage
"zone_B": 30, # percentage
},
"satellite_imagery": {
"vegetation_health_index": 0.85, # normalized between 0 to 1
},
"weather_forecast": {
"today": {"temperature": 28, "humidity": 65, "precipitation": 3}, # in °C, %, mm
"next_week_precipitation": 15, # mm of rain expected over the next week
}
}
# Describe data for LLM input
data_summary = (
f"Zone A soil moisture is at {farm_data['soil_moisture']['zone_A']}%, while Zone B is at {farm_data['soil_moisture']['zone_B']}%. "
f"The satellite imagery shows a vegetation health index of {farm_data['satellite_imagery']['vegetation_health_index']}. "
f"Today's weather forecast indicates a temperature of {farm_data['weather_forecast']['today']['temperature']}°C, "
f"with 65% humidity and 3mm precipitation. The forecasted rainfall for the next week is 15mm."
)
# Use LLM to generate sustainable irrigation and fertilization recommendations
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI agricultural assistant specializing in sustainable precision farming."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the following data, provide sustainable irrigation and fertilization recommendations: {data_summary}"}
]
)
recommendations = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(recommendations)
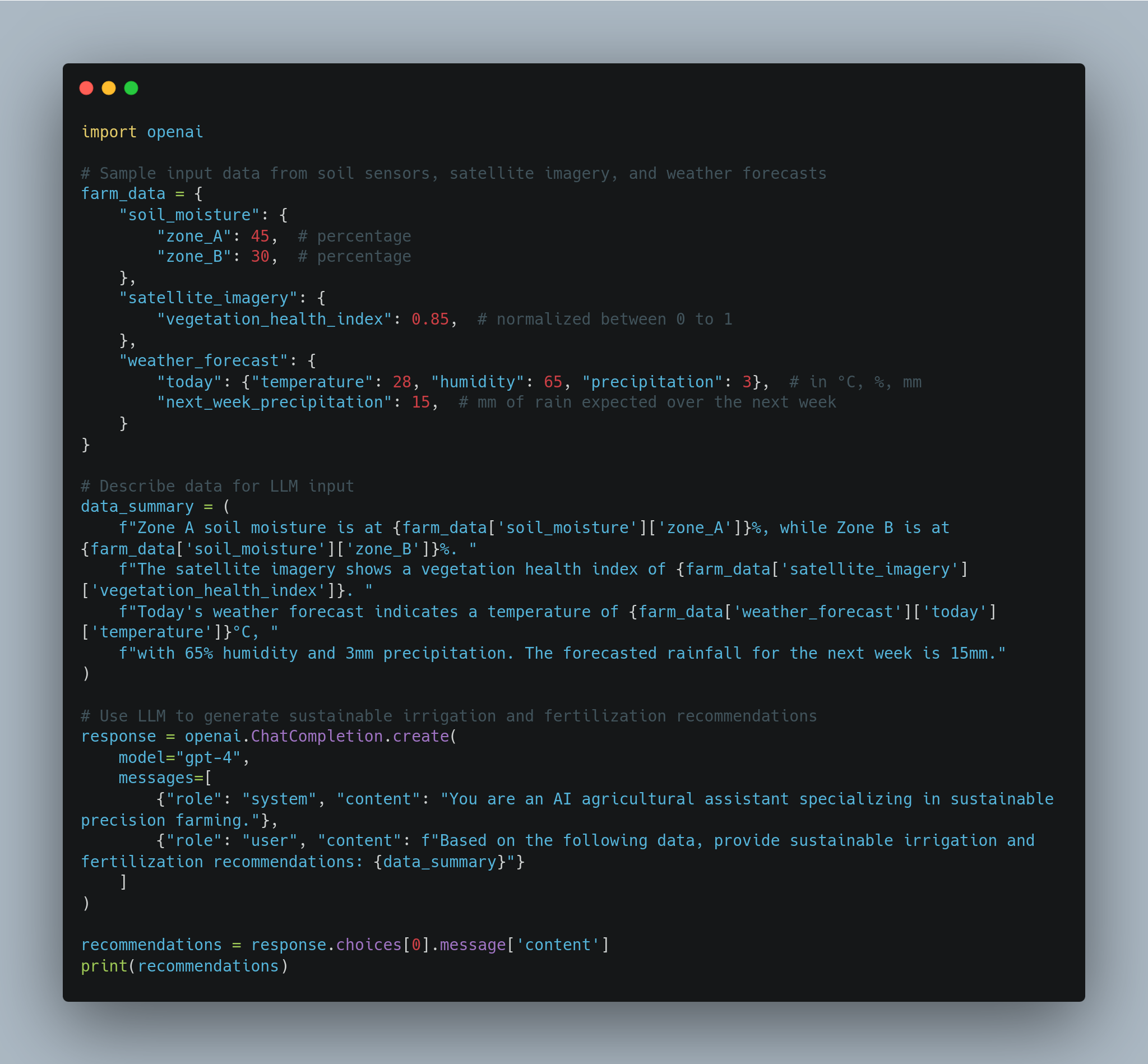
**Sustainable Irrigation and Fertilization Recommendations:**
- **Zone A Irrigation:** Since soil moisture is at 45%, no immediate irrigation is needed. Reassess after the next rainfall. Depending on the forecasted 15mm rain, irrigation may not be necessary for at least 5 days.
- **Zone B Irrigation:** Soil moisture in Zone B is at 30%, which is approaching a critical threshold. Schedule light irrigation (20mm) for Zone B tomorrow to maintain optimal soil moisture, then reassess after the next week's rain.
- **Fertilization Strategy:** The vegetation health index of 0.85 indicates good crop health. Continue applying fertilizer at 60% of the standard rate, focused only in areas of Zone B where soil nutrient data indicates low nitrogen. This approach will reduce overuse of fertilizers and protect the soil from degradation.
Example 2: AI-powered farm management software for crop monitoring and anomaly detection
Objective: Integrate an LLM with AI-powered farm management software that uses computer vision and predictive analytics to identify crop anomalies like nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations and provide sustainable intervention strategies.
import openai
# Sample data from farm management software using computer vision for anomaly detection
crop_data = {
"drone_images": {
"zones": {
"zone_1": {"anomaly_detected": "nitrogen deficiency", "severity": "moderate"},
"zone_2": {"anomaly_detected": "early-stage pest infestation", "severity": "low"}
}
},
"crop_health": {
"growth_stage": "mid-vegetative",
"projected_yield": 4000 # kg/ha
}
}
# Describe data for LLM input
crop_data_summary = (
f"Drone images have detected a nitrogen deficiency in Zone 1, with moderate severity, and an early-stage pest infestation in Zone 2, with low severity. "
f"The crops are in the mid-vegetative growth stage, and the projected yield is currently 4000 kg/ha."
)
# Use LLM to generate sustainable recommendations for addressing detected anomalies
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI expert specializing in sustainable crop monitoring and intervention strategies."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the detected anomalies and current crop health, provide sustainable intervention strategies: {crop_data_summary}"}
]
)
sustainable_strategy = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(sustainable_strategy)
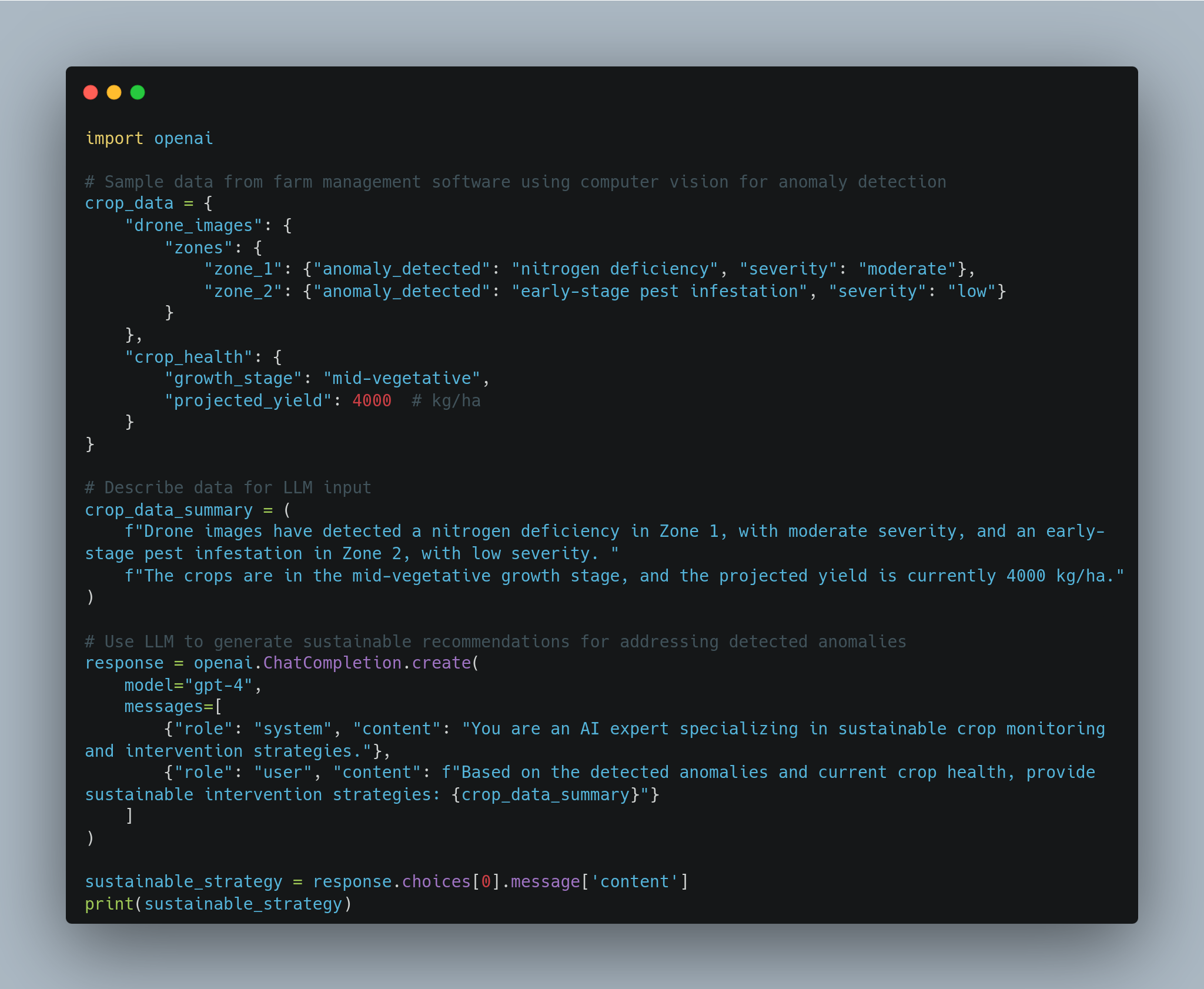
**Sustainable Intervention Strategies:**
- **Zone 1 Nitrogen Deficiency:** Apply a nitrogen-rich organic fertilizer such as composted manure to address the deficiency in a sustainable manner. Spread the fertilizer evenly across the affected area, ensuring a slow-release approach to prevent nitrogen runoff and soil contamination.
- **Zone 2 Pest Infestation:** Given the early stage and low severity of the pest infestation, implement biological pest control methods such as introducing natural predators or using neem oil to minimize chemical pesticide use. Continue monitoring the affected area closely for any escalation in pest activity.
- **General Management:** Maintain regular soil testing and drone-based monitoring to ensure nutrient levels are balanced and pest control measures are effective. This proactive approach will protect yield potential while minimizing environmental impact.
Example 3: AI-enhanced predictive analytics for climate-adaptive sustainable farming
Objective: Use LLM to analyze predictive climate data and provide sustainable, climate-adaptive strategies for planting, crop selection, and soil management. The goal is to optimize land use in light of changing weather patterns and minimize environmental risks.
import openai
# Sample predictive climate data and historical trends
climate_data = {
"historical_weather": {
"average_temp_summer": 32, # °C
"average_rainfall_summer": 80 # mm/month
},
"predictive_weather_model": {
"next_summer": {"projected_temp": 35, "projected_rainfall": 50}, # °C, mm
"risk_assessment": {"drought_risk": "high", "heatwave_risk": "moderate"}
},
"soil_data": {
"organic_matter": 2.5, # percentage
"soil_type": "loamy",
"moisture_retention": "moderate"
}
}
# Describe data for LLM input
climate_data_summary = (
f"Historically, the average summer temperature has been 32°C with 80mm of rainfall per month. "
f"However, next summer's predictive model suggests temperatures may rise to 35°C with reduced rainfall of 50mm. "
f"There is a high risk of drought and a moderate risk of heatwaves. The soil is loamy with 2.5% organic matter and moderate moisture retention."
)
# Use LLM to generate climate-adaptive, sustainable land use strategies
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI expert in sustainable land use and climate-adaptive farming."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Based on the predictive climate and soil data, provide sustainable, climate-adaptive farming strategies: {climate_data_summary}"}
]
)
climate_adaptive_strategy = response.choices[0].message['content']
print(climate_adaptive_strategy)
**Climate-Adaptive Sustainable Farming Strategies:**
- **Crop Selection:** Choose drought-resistant crop varieties such as sorghum, millet, or certain legumes that are well-suited to withstand higher temperatures and lower rainfall. Consider crop rotation that improves soil health and enhances water retention.
- **Soil Management:** Improve soil organic matter content by incorporating cover crops or applying organic compost. This will enhance soil moisture retention and provide a buffer against heatwaves and drought conditions. Mulching is also recommended to conserve soil moisture and reduce evaporation.
- **Irrigation Strategy:** Given the high risk of drought, implement drip irrigation systems to deliver water directly to the plant roots, maximizing water efficiency. Utilize AI-powered precision irrigation tools to monitor real-time soil moisture and minimize water waste.
- **Heatwave Mitigation:** Use shade cloth or other protective structures during the peak heat periods to shield sensitive crops from excessive heat stress. Additionally, schedule irrigation during early morning or late evening to reduce water loss due to evaporation.
In Example 1, we used LLMs to analyze data from sensors, satellite imagery, and weather forecasts to optimize irrigation and fertilizer use, focusing on sustainable land use and conservation of resources.
In Example 2, LLMs helped detect crop anomalies (such as nutrient deficiencies and pest infestations) through computer vision, providing sustainable, targeted interventions that minimize chemical use and prevent further damage.
And in Example 3, LLMs helped us analyze predictive climate models and soil data to offer sustainable land use strategies, advising farmers on adaptive practices that mitigate the risks of drought and heatwaves, promote soil health, and optimize resource use.
In these examples, LLMs enhanced decision-making in agriculture by processing complex data and providing actionable, sustainable strategies that increased productivity while reducing environmental impact. These AI-enhanced systems promote the long-term sustainability of agricultural practices.
The integration of AI technologies in sustainable land use strategies holds transformative potential for the agricultural sector. Precision agriculture, AI-powered farm management software, and sustainable farming practices driven by AI collectively optimize resource management, enhance crop yield, and minimize environmental impact.
Financial incentives further support the adoption of these technologies, making sustainable farming practices accessible to a broader range of farmers.
As we embrace the future of agriculture with AI, we move towards a more efficient, productive, and environmentally conscious approach to farming. By leveraging data-driven insights and innovative solutions, farmers can contribute to building a resilient and sustainable food system that meets the needs of a growing global population. The journey towards sustainable agriculture is not without challenges, but with AI as a powerful ally, we are well-equipped to navigate these challenges and shape a prosperous future for farming.