
AWS Security Specialty Certification: How to Prepare for the Exam
AWS Security Specialty Certification: How to Prepare for the Exam 관련

Welcome to my latest tutorial! After a three-year hiatus from certifications, I'm thrilled to announce that I've successfully obtained the AWS Certified Security Specialty certification. As someone who strongly believes in the power of community learning, I'm excited to share my journey and insights with you.
In this guide, I'll take you through my experience of preparing for and passing the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam. Rather than a comprehensive study guide, I'll present this as a collection of study notes and personal observations. My aim is to provide you with practical tips and strategies that helped me succeed.
For those seeking a more structured approach, I highly recommend the official AWS certification study guide and the excellent resources provided by TutorialsDojo. These were invaluable in my preparation and could be great resources for your own journey.
So, whether you're considering this certification or you’re just curious about AWS security, I hope you'll find value in the experiences and insights I'm about to share.
Should You Get Certified?
There are mixed opinions in the tech industry about the importance of certifications. Some people argue that the certificates you have don't matter - it's all about your real-world knowledge.
But not everyone has the chance to work with real-world projects. And certification questions are based on real-world scenarios. So if you haven't had an opportunity to work with AWS security much in practice, you can learn from this exam and apply your learnings on actual projects.
On the other hand, if you're already working with AWS, taking the exam is an excellent chance to test your knowledge and learn more about its internal workings.
For example, you might have been working with AWS for quite some time, but you haven't touched AWS security, or haven't been following best practices. The certification covers every aspect of AWS security, so you will learn how you can reduce your costs and follow best practices.
Exam Structure
- Exam Duration: 170 Mins
- Exam Format: 65 Questions. Multiple Choice, Multiple response
- Passing Score: The exam uses a scaled scoring system from 100 to 1,000. To pass, you need to achieve a minimum score of 750.
- Cost: $300 USD. Additional Tax may be $30.
- Delivery Method: Pearson VUE testing center or online proctored exam
It took me about 110 minutes to finish the questions, and I marked 25 for review. I then spent another 60 minutes reviewing those 25 questions.
In my case, the internet got disconnected, and my exam froze. Don't panic! Just launch the VUE software again—you are allowed to resume the exam. No snacking or restroom breaks are allowed, but you can have water.
My Study Approach
I used a structured method to prepare for the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam:
- Completed a comprehensive AWS security course on Udemy
- Practiced with multiple sets of exam questions:
- Carefully analyzed incorrect answers
- Consulted AWS documentation and AWS YouTube videos for a deeper understanding
- Used additional practice resources:
- TutorialsDojo practice exams
- WhizLabs mock tests
This approach helped me gain both theoretical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills essential for the exam.
Key Topics and Concepts
AWS IAM Credential Report
Understanding how to review the AWS IAM credential report is crucial. Here are some key points:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Enforcement: Identify users who haven't enabled MFA and enforce its usage.
- Root Account Monitoring: Monitor usage of the root account to ensure it's not being used for day-to-day operations.
- Track user creation and last activity dates to manage user lifecycles effectively.
- Access Key Usage Monitoring: Identify unused access keys that could pose a security risk.
- Find users with old passwords or access keys that might be compromised.
- Understand Report Format: AWS Documentation
AWS S3 Object Lock
AWS S3 Object Lock is a feature that helps prevent objects from being deleted or overwritten for a fixed amount of time or indefinitely. It's particularly useful for scenarios requiring data immutability, such as regulatory compliance or protection against accidental or malicious deletion.
- Compliance Mode: Prevents anyone, including the root user, from overwriting or deleting an object version.
- Governance Mode: Allows users with special permissions to overwrite or delete protected object versions.
Integrating On-Premise Active Directory with IAM
It's important to know the steps involved in integrating on-premise Active Directory with IAM for single sign-on. For more details, refer to this AWS Blog Post.
AWS Service Control Policies (SCPs)
Study AWS SCP examples. Service Control Policies (SCPs) are organization-level policies that manage permissions across your AWS organization. They provide centralized control over the maximum available permissions for IAM users and roles within your organization's accounts.
For SCP examples, refer to the AWS Documentation.
Serving Private Content through CloudFront
Learn how to serve private content through CloudFront. The AWS CloudFront Developer Guide provides detailed information on this topic.
- Using signed URLs is beneficial when you want to restrict access to individual files, for example, an installation download for your application.
- Using signed cookies is beneficial when you want to provide access to multiple restricted files, and don't want to change your current URLs.
Understanding Ephemeral Ports
Understand why it's important to set the range for ephemeral ports in outbound rules. Ephemeral ports are temporary ports used in network and internet communications, managed by the machine's operating system.
Check out this Medium article (remy-nts) on NACL and ephemeral ports.
Securing Access to Websites through CloudFront
To ensure that users can only access your website through the CloudFront URL while completely restricting access via the Application Load Balancer (ALB) URL, you’ll need to know how to do the following:
- Configure ALB Security Group: Restrict access to your ALB by only allowing traffic from CloudFront IP ranges.
- Implement Custom Headers: Set a custom header in CloudFront and configure your ALB to only accept requests with this header.
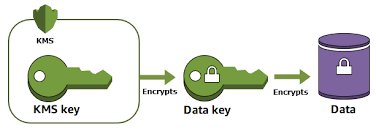
AWS KMS and Envelope Encryption
AWS KMS can directly encrypt data up to 4 KB in size. For files larger than 4 KB, you need to use Envelope Encryption. Here are the steps:
- Generate a data key using AWS KMS
- Use the data key to encrypt your large data
- Encrypt the data key with KMS
- Store the encrypted data key with your encrypted data
KMS Policy Conditions
Learn how conditions work in AWS KMS policy. Refer to the AWS KMS Developer Guide for detailed information.
IAM Policy Conditions
- Get to know important IAM policy conditions. The AWS IAM User Guide offers detailed information.
- I strongly suggest watching these two videos to understand IAM policy conditions with examples:
Lambda Function Assuming IAM Role in Another AWS Account
Understand how to configure a Lambda function to assume an IAM role in another AWS account. Refer to this AWS Knowledge Center article for details.
KMS Key Rotation
Understand which types of keys can be rotated automatically and which require manual rotation.
- Symmetric encryption KMS keys can be rotated automatically.
- Asymmetric KMS keys, HMAC KMS keys, and custom key stores require manual rotation.
- KMS keys with imported key material also require manual rotation.
For more information, see the AWS KMS Developer Guide.
Amazon ECR Image Scanning
You can scan Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) images for vulnerabilities. There are two types of scanning available in ECR:
- Enhanced scanning—Amazon ECR integrates with Amazon Inspector to provide automated, continuous scanning of your repositories. Enhanced scanning provides the following:
- OS and programming languages package vulnerabilities.
- Two scanning frequencies: Scan on push and continuous scan.
- Basic scanning—Amazon ECR provides two versions of basic scanning that use the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) database:
- The current GA version, which uses the open-source Clair project
- An improved version that uses AWS native technology
Basic scanning offers:
- OS scans
- Two scanning frequencies: manual and scan-on-push
Implementing End-to-End Encrypted Traffic
Know when you have a use case that requires implementing end-to-end encrypted traffic. Steps are listed below:
- Configure your CloudFront distribution to require HTTPS for all viewer requests.
- Use a custom SSL/TLS certificate (from AWS Certificate Manager or imported) for CloudFront.
- Use a third-party SSL/TLS certificate on your Application Load Balancer (ALB) or EC2 instances.
- Ensure you use the same certificate on your EC2 instances as on your ALB for consistency.
Securely Storing RDS Credentials
Learn how to securely store RDS credentials. AWS Secrets Manager is the recommended service for storing and managing sensitive information like database credentials. It is not wise to hard-code database credentials in your code or store them in Lambda as environment variables.
CloudTrail: Data Events vs Management Events
Understand the differences between data events and management events in CloudTrail.
Management Events
- Provide information about management operations performed on resources in your AWS account.
- Examples include:
- IAM AttachRolePolicy operations
- Amazon EC2 CreateSubnet operations
- AWS CloudTrail CreateTrail operations
Data Events
- Provide information about resource operations performed on or within a resource.
- Examples include:
- Amazon S3 object-level API activity
- AWS Lambda function execution activity
- Amazon DynamoDB object-level API activity on tables
- Data events are not logged by default.
GuardDuty: Suppression Rules, Trusted IP Lists, and Threat Lists
Expect questions about suppression rules and how to add known IPs to trusted IP lists and threat lists during penetration testing.
Understand which logs are analyzed by AWS GuardDuty. These include AWS CloudTrail management event logs, VPC Flow Logs, DNS logs, EKS audit logs, S3 data events, and runtime activity from EKS, EC2, and ECS workloads.
AWS Abuse Email
Know how to respond to an AWS abuse email.
- Review the abuse notice carefully to understand what content or activity was reported. The report typically includes logs or other evidence implicating the abusive activity.
- Investigate the reported issue within your AWS resources.
- Verify and understand the cause of the reported abuse.
- Take immediate action to stop or prevent the abusive activity. This may involve:
- Removing or modifying offending content
- Securing compromised resources
- Updating security settings
- Revoking unauthorized access
Inspector
You need to know which AWS services are scanned by AWS Inspector.
- Amazon Inspector can evaluate:
- EC2 instances
- Container images in Amazon ECR
- Lambda functions for vulnerabilities and security issues
The following AWS services integrate with Amazon Inspector:
- AWS Security Hub for a centralized view of security findings
- Amazon EventBridge for automated responses to findings
- AWS Systems Manager for patch management based on Inspector findings
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) for container image scanning
AWS Config
Learn these important AWS Config rules:
- encrypted-volumes: Checks if attached EBS volumes are encrypted.
- s3-bucket-public-read-prohibited: Ensures that your S3 buckets do not allow public read access.
- iam-user-no-policies-check: Verifies that IAM users don't have policies directly attached to them (best practice is to use group policies).
- root-account-mfa-enabled: Checks if the root account has Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enabled.
- ec2-instances-in-vpc: Ensures that all EC2 instances are launched within a VPC.
- cloudtrail-enabled: Verifies that CloudTrail is enabled in your account.
- rds-instance-public-access-check: Checks if RDS instances are not publicly accessible.
- iam-password-policy: Ensures that the account password policy meets specified complexity requirements.
- restricted-ssh: Checks if security groups allow unrestricted incoming SSH traffic.
- cloudwatch-alarm-action-check: Verifies if CloudWatch alarms have at least one alarm action, one
INSUFFICIENT_DATAaction, or one OK action enabled.
For more details, refer to the AWS Config Managed Rules documentation.
Trusted Advisor
Be aware of the checks performed by AWS Trusted Advisor:
- Security Groups - Specific Ports Unrestricted: Identifies security groups that allow unrestricted access to specific ports, potentially exposing your resources to security risks.
- IAM Use: Ensures that you're following security best practices by using IAM users, groups, and roles to control access to your AWS resources, rather than using your root account credentials.
- MFA on Root Account: Verifies if multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled on your AWS account's root user, significantly enhancing security.
- EBS Public Snapshots: Identifies EBS snapshots that are publicly accessible, which could lead to unintended data exposure.
- RDS Public Snapshots: Similar to the EBS check, identifies RDS snapshots that are publicly accessible.
- S3 Bucket Permissions: Checks for S3 buckets with open access permissions or those that allow access to any authenticated AWS user.
- CloudTrail Logging: Verifies if CloudTrail is enabled for all regions, crucial for maintaining an audit trail of actions taken on your AWS account.
- IAM Password Policy: Checks if your IAM password policy aligns with security best practices, such as minimum length and complexity requirements.
- Exposed Access Keys: Identifies if any of your AWS access keys have been exposed publicly on code repositories or other public sites.
- Security Groups - Unrestricted Access: Checks for security groups that allow unrestricted access (0.0.0.0/0) to specific ports.
S3 Encryption
Learn about the different use cases for S3 encryption options.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE)
- This is the default encryption method for all new buckets and objects.
- Amazon S3 handles key management and encryption/decryption automatically.
- Uses AES-256 encryption algorithm.
- Each object is encrypted with a unique key, and the key itself is encrypted with a regularly rotated master key.
- SSE-KMS (Server-Side Encryption with AWS KMS-Managed Keys)
- Uses AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for managing encryption keys.
- Provides additional control and audit trail for your keys.
- Allows you to use customer-managed keys (CMKs) or AWS managed keys.
- Enables you to set key rotation policies and control key usage through IAM policies.
- SSE-C (Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys)
- You manage your own encryption keys.
- S3 performs the encryption/decryption, but you provide the key with each request.
- Keys are not managed by AWS; you must provide the correct key to access the object.
- Client-Side Encryption
- Data is encrypted before sending it to S3.
- You can use the Amazon S3 Encryption Client or implement your own client-side encryption.
- Provides end-to-end encryption, as data is encrypted before leaving your application.
For more information, watch this video.
CloudFormation and Secrets
Using secrets in AWS CloudFormation is a great way to manage sensitive information securely. CloudFormation supports dynamic references to secrets stored in AWS Secrets Manager.
In the example below, MySecret:{{resolve:secretsmanager:SecretName:SecretKey:VersionStage:VersionId}} retrieves the 'password' field from the secret 'MySecretName' in Secrets Manager.
MySecret:
Type: AWS::SecretsManager::Secret
Properties:
Name: MySecretName
Description: "This is my secret"
SecretString: '{"username":"myuser","password":"mypassword"}'
VPC FlowLog
Understand the use cases for using VPC flow logs.
- Identify unusual traffic patterns or unexpected denied connections.
- Detect potential security threats by identifying suspicious IP addresses or unusual port activity.
- You can set up automated alerts using CloudWatch Alarms for specific traffic patterns.
2 123456789010 eni-1234567890abcdef0 10.0.1.5 10.0.0.220 39812 80 6 20 4249 1418530010 1418530070 ACCEPT O
Let's break down this log entry:
- Version number (2)
- AWS account ID (123456789010)
- Network interface ID (eni-1234567890abcdef0)
- Source IP address (10.0.1.5)
- Destination IP address (10.0.0.220)
- Source port (39812)
- Destination port (80)
- Protocol (6 = TCP)
- Packets transferred (20)
- Bytes transferred (4249)
- Start time (1418530010)
- End time (1418530070)
- Action (ACCEPT)
- Log status (0)
S3 Glacier Vault Lock Policies and Archival Retrieval Options
S3 Glacier Vault Lock policies are a powerful feature for enforcing compliance controls on your Amazon S3 Glacier vaults. These policies allow you to create and lock down rules that control access to your archives, ensuring that your data retention and deletion policies are strictly enforced.
When initiating a job to retrieve an archive, you can specify one of the following retrieval options, based on your access time and cost requirements.
- Expedited: Expedited retrievals allow you to quickly access your data that's stored in the S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval storage class or the S3 Intelligent-Tiering Archive Access tier when occasional urgent requests for restoring archives are required. For all but the largest archives (more than 250 MB), data accessed by using Expedited retrievals is typically made available within 1-5 minutes. Provisioned capacity ensures that retrieval capacity for Expedited retrievals is available when you need it.
- Standard: Standard retrievals allow you to access any of your archives within several hours. Standard retrievals are typically completed within 3-5 hours. Standard is the default option for retrieval requests that do not specify the retrieval option.
- Bulk: Bulk retrievals are the lowest-cost S3 Glacier retrieval option, which you can use to retrieve large amounts, even petabytes, of data inexpensively in a day. Bulk retrievals are typically completed within 5-12 hours.
RDS Copying Encrypted Snapshots
- You can’t share snapshots that are encrypted with the default AWS managed key. You can only share snapshots that are encrypted with a customer-managed key.
- You can share only unencrypted snapshots publicly.
- When you share an encrypted snapshot, you must also share the customer-managed key used to encrypt the snapshot.
- Since you cannot share a snapshot that is encrypted with the default AWS managed key, you can copy the snapshot first. When you copy a snapshot, you can encrypt the copy or you can specify a KMS key that is different than the original, and the resulting copied snapshot uses the new KMS key.
- Also, you cannot enable encrypt snapshots on existing RDS.
WAF Protections
Understand which layer AWS WAF operates on. AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) mainly works at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model.
AWS Config Aggregator
You can expect questions about AWS Config Aggregator. This feature lets you gather configuration and compliance data from multiple accounts and regions into one account, giving you a complete view of your AWS resources.
For more information, refer to the AWS Config Aggregator documentation.
AWS Macie
Learn how to categorize your data using Amazon Macie.
- Macie can automatically scan your S3 buckets to identify sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property.
- Macie helps assess and monitor the security posture of your S3 buckets, identifying misconfigurations or overly permissive access policies.
- Automatically classify data based on its sensitivity, helping organizations manage and protect data according to its importance.
AWS CloudFront OAI
Learn how to restrict user access to content directly from S3. To limit user access to content directly from S3 when using Amazon CloudFront, you can use Origin Access Identity (OAI). An OAI is a special CloudFront user that lets you restrict access to your S3 bucket content. When you create an OAI, CloudFront connects it to your distribution, and you can configure your S3 bucket to only allow access from that OAI.
AWS CloudHSM
Use AWS CloudHSM instead of KMS when you want complete control over key management hardware and keys.
AWS CloudHSM lets you manage and use your keys on FIPS-approved hardware. It uses customer-owned, single-tenant HSM instances that operate in your own Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). If you need full control over the Hardware Security Module (HSM) that stores and manages your cryptographic keys, CloudHSM is the better choice.
AWS KMS Key Types
Learn about the available KMS key types:
- Symmetric Keys
- AWS Managed Keys
- Customer Managed Keys
- Asymmetric Keys: These consist of a public and private key pair.
- HMAC Keys: Used for generating and verifying Hash-based Message Authentication.
- Multi-Region Keys: A set of interoperable keys that can be replicated across multiple AWS Regions. These are useful for encrypting data across multiple Regions or for disaster recovery scenarios.
- Keys with Imported Key Material: Allows you to import your own key material into KMS.
- Keys in Custom Key Stores: Enables you to create and manage KMS keys in an AWS CloudHSM cluster.
A Few Notes on AWS CloudTrail
- Enable CloudTrail in all regions: To ensure thorough logging, activate CloudTrail in every AWS region. This gives you a complete record of activities across your entire AWS infrastructure.
- Use a dedicated S3 bucket: Store CloudTrail logs in a specific S3 bucket with strict access controls. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures the integrity of your audit logs.
- Enable log file integrity validation: This feature uses industry-standard algorithms to ensure that your log files haven't been tampered with after delivery to S3.
- Encrypt log files: Use server-side encryption with AWS KMS managed keys (SSE-KMS) to secure your CloudTrail log files while they are stored. This provides an additional layer of security for your audit data.
- For the S3 bucket that stores CloudTrail logs, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Delete. This helps prevent unauthorized deletion of log files.
- Use AWS Config rules to make sure CloudTrail is always turned on and set up correctly across all your accounts.
- Regularly review and analyze your CloudTrail logs. Consider using AWS services like Amazon Athena or third-party SIEM tools for log analysis.
- If you're using AWS Organizations, consider setting up organization-wide trails to centralize logging for all accounts in your organization.
S3 Replication
Learn how to replicate encrypted S3 objects across regions.
- Versioning must be enabled on both source and destination buckets.
- Create a replication role: Create an IAM role that allows S3 to assume the role and perform replication tasks.
- Attach a policy to the replication role: This policy should grant permissions to read from the source bucket and write to the destination bucket.
- You can set up replication using the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI.
- KMS Key Permissions: If you're using AWS KMS for encryption, you need to grant the replication role permission to use the KMS key in both the source and destination regions.
AWS Service Catalog
Learn about the use cases for AWS Service Catalog.
You can use AWS Service Catalog to standardize your applications and distribute them to your teams. For example, if you want to set restrictions on encryption and AMIs, you can create a complete application stack and share it with your team.
MFA for Active Directory Users
You can enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory to increase security when your users specify their AD credentials to access supported Amazon Enterprise applications.
When you enable MFA, your users enter their username and password (first factor) as usual, and they must also enter an authentication code (the second factor) they obtain from your virtual or hardware MFA solution.
AWS IAM Access Analyzer
- Cross-Account Access Analysis: Helps identify resources that are shared with external AWS accounts, ensuring only intended cross-account access exists.
Conclusion
Getting the AWS Certified Security Specialty certification was a great experience that helped me learn more about AWS security. By studying and applying what I learned, I gained useful knowledge about keeping AWS environments secure.
This certification proved my skills and gave me the tools to use best practices in real situations. Whether you're new to AWS security or want to improve your skills, going for this certification can be an important part of your career growth.
I hope my experiences encourage and help you on your certification path. Keep in mind that ongoing learning and being active in the community are important to stay updated in the fast-changing world of cloud security.