
How to Build a Simple Bitcoin-to-USD Calculator
How to Build a Simple Bitcoin-to-USD Calculator 관련


Welcome to this fun and hands-on project where we'll build a calculator that converts Bitcoin to USD. You'll learn about API fetching, DOM manipulation, and localStorage, and you'll use some basic math along the way.
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a functioning Bitcoin price calculator that fetches the current price of Bitcoin, allows you to calculate the value of your Bitcoin holdings, and saves your data locally.
This is a beginner-friendly project suited for those who understand the basics of HTML, CSS, and vanilla JavaScript.
This is what we'll create:

Project Setup
Create a new folder and name it something relevant to the project, such as btc-usd-calc. Create a file titled index.html in your project folder.
Start by writing the HTML. The page should essentially contain
- A heading
- The current Bitcoin price
- A text field for a user to input their Bitcoin holdings
- A button to calculate their Bitcoin holdings
- The calculated amount
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Bitcoin Calculator</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Bitcoin Calculator</h1>
<main id="main">
<p>
<span id="currentPrice">Latest price:</span>
<b>$<span id="bitcoinPrice"></span> USD</b>
</p>
<label for="bitcoinAmount">How much Bitcoin do you own?</label>
<input type="number" id="bitcoinAmount" step="any" placeholder="0.05" />
<button id="calculateBtn">Calculate</button>
<br />
<br />
<h3 id="usdAmount"></h3>
</main>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Open it up in a browser and you should see this:

Fetch the API
Now, in the same directory as index.html, create a new file titled script.js.
It's important to know what API to use. I highly recommend that you use this one while following along with this tutorial. The CoinDesk API is:
- Free
- Fast
- No API token needed
- Minimal
- Contains the necessary information for this project
In script.js, define a constant for the API URL:
const API_URL = "https://api.coindesk.com/v1/bpi/currentprice.json";
The next thing to do is to add an event listener to call the API once the page content loads. You can do that by adding the following code directly underneath the API_URL constant:
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", async () => {
// Run an asynchronous function once the DOM content has loaded
let bitcoinPrice; // Initialize the variable
try {
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
// Await a response from the HTTP request sent to the API URL
const data = await response.json();
// Await the json content of the response
bitcoinPrice = data.bpi.USD.rate_float.toFixed(2);
// Reassign the bitcoinPrice variable to the USD value of Bitcoin, rounded to the nearest 2 decimal places.
} catch {
console.log("error!"); // In case of error
}
console.log(bitcoinPrice); // Log the price in the console
});
In case of any errors, the program will let us know in the console. Otherwise, bitcoinPrice will be logged in the console. You can test it out now and see if you get the current Bitcoin price!
-how-to-implement-localstorage">How to Implement localStorage
Fundamentally, localStorage is a feature in most web browsers (see which versions support it here) that saves information so that it is retained in the browser's memory even after the page or browser is closed.
Let's get started by editing some lines:
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", async () => {
let bitcoinPrice = localStorage.getItem("lastBitcoinPrice");
// Retrieve the last stored Bitcoin price from localStorage, if it exists
// Note: It should be null the first time you try running the page
try {
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
const data = await response.json();
bitcoinPrice = data.bpi.USD.rate_float.toFixed(2);
// bitcoinPrice will be re-written
localStorage.setItem("lastBitcoinPrice", bitcoinPrice);
// Save most recent price to localStorage
} catch {
console.log("error!");
}
console.log(bitcoinPrice);
});
How to Implement DOM Manipulation
The Document Object Model (DOM) is an interface that allows programming interactions with web documents. Essentially, DOM manipulation with JavaScript allows us to update certain parts or the entirety of a document.
In this project, we'll use it to show the current Bitcoin price and calculated value. We'll also use it to retrieve the user-inputted value in the #bitcoinAmount text field when the calculate button is clicked.
Let's implement DOM manipulation:
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", async () => {
const main = document.getElementById("main");
const bitcoinPriceElement = document.getElementById("bitcoinPrice");
const bitcoinAmountInput = document.getElementById("bitcoinAmount");
const calculateBtn = document.getElementById("calculateBtn");
const usdAmountElement = document.getElementById("usdAmount");
let bitcoinPrice = localStorage.getItem("lastBitcoinPrice");
try {
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
const data = await response.json();
bitcoinPrice = data.bpi.USD.rate_float.toFixed(2);
localStorage.setItem("lastBitcoinPrice", bitcoinPrice);
bitcoinPriceElement.textContent = bitcoinPrice;
// Set the text content of bitcoinPriceElement to the current bitcoinPrice
} catch {
if (bitcoinPrice) {
// If there's an existing bitcoinPrice in localStorage...
bitcoinPriceElement.textContent = bitcoinPrice;
// ...display whatever is saved localStorage
} else {
main.innerHTML = "<p>Could not fetch Bitcoin price :(</p>";
return;
}
}
console.log(bitcoinPrice);
});
How to Calculate the Current Wallet Value
Now, the point of a Bitcoin calculator is to calculate how much someone's Bitcoin wallet is valued, not necessarily how much the current price is.
For example, the current price of Bitcoin might be $60,000 USD. If you own 2 Bitcoins, your wallet is valued at $120,000 USD. If you own half (0.5) a Bitcoin, your wallet is valued at $30,000 USD.
Let's get the amount of Bitcoin that the user owns (bitcoinAmount) from localStorage.
// continue after console.log(bitcoinPrice);
let bitcoinAmount = localStorage.getItem("bitcoinAmount");
Calculate the amount in USD with this function:
const calculateUSDAmount = () => {
bitcoinAmount = bitcoinAmountInput.value || 0;
// bitcoinAmount will be reassigned to whatever is in the input on the front end, otherwise it's default value will be zero
const usdAmount = bitcoinAmount * bitcoinPrice;
// Say you have 2 Bitcoins and the price is 60000.
// 2 * 60000 = 120000
usdAmountElement.innerHTML = `<b>$${usdAmount.toFixed(
2
)} USD</b> worth of Bitcoin.`;
// Round it to the nearest 2 decimals and display it
};
Remember when we got bitcoinAmount from localStorage? Now, when the page loads, let's set the value of the input on the front-end to bitcoinAmount.
if (bitcoinAmount) {
bitcoinAmountInput.value = bitcoinAmount;
// Set the input's value to bitcoinAmount
calculateUSDAmount();
// Calculate and update the front-end
}
For the user to update their bitcoinAmount, let's add an event listener to when the calculateBtn is clicked:
calculateBtn.addEventListener("click", () => {
localStorage.setItem("bitcoinAmount", bitcoinAmountInput.value);
// Save the input value to localStorage
calculateUSDAmount();
// Calculate and update the front-end
});
All of the JavaScript should now be complete.
Full JavaScript Code
You entire code should be similar to this (aside from comments and formatting):
const API_URL = "https://api.coindesk.com/v1/bpi/currentprice.json";
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", async () => {
const main = document.getElementById("main");
const bitcoinPriceElement = document.getElementById("bitcoinPrice");
const bitcoinAmountInput = document.getElementById("bitcoinAmount");
const calculateBtn = document.getElementById("calculateBtn");
const usdAmountElement = document.getElementById("usdAmount");
let bitcoinPrice = localStorage.getItem("lastBitcoinPrice");
try {
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
const data = await response.json();
bitcoinPrice = data.bpi.USD.rate_float.toFixed(2);
localStorage.setItem("lastBitcoinPrice", bitcoinPrice);
bitcoinPriceElement.textContent = bitcoinPrice;
// Set the text content of bitcoinPriceElement to the current bitcoinPrice
} catch {
if (bitcoinPrice) {
// If there's an existing bitcoinPrice in localStorage...
bitcoinPriceElement.textContent = bitcoinPrice;
// ...display whatever is saved localStorage
} else {
main.innerHTML = "<p>Could not fetch Bitcoin price :(</p>";
return;
}
}
console.log(bitcoinPrice);
let bitcoinAmount = localStorage.getItem("bitcoinAmount");
const calculateUSDAmount = () => {
bitcoinAmount = bitcoinAmountInput.value || 0;
// bitcoinAmount will be reassigned to whatever is in the input on the front end, otherwise it's default value will be zero
const usdAmount = bitcoinAmount * bitcoinPrice;
// Say you have 2 Bitcoins and the price is 60000.
// 2 * 60000 = 120000
usdAmountElement.innerHTML = `<b>$${usdAmount.toFixed(
2
)} USD</b> worth of Bitcoin.`;
// Round it to the nearest 2 decimals and display it
};
if (bitcoinAmount) {
bitcoinAmountInput.value = bitcoinAmount;
// Set the input's value to bitcoinAmount
calculateUSDAmount();
// Calculate and update the front-end
}
calculateBtn.addEventListener("click", () => {
localStorage.setItem("bitcoinAmount", bitcoinAmountInput.value);
// Save the input value to localStorage
calculateUSDAmount();
// Calculate and update the front-end
});
});
Test it out in the browser and play around with it!

How to Add Some Styling
Right now, there isn't any CSS so it looks pretty basic. You're more than welcome to customize the styling to your own preferences.
If you'd like to style it how I did, then follow along by adding this line at the bottom of <head>:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
</head>
Then, create a new file titled style.css within the same directory as index.html.
Write the following code in style.css:
@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:wght@400;700&display=swap");
body {
font-family: "Inter", sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.container {
max-width: 50rem;
margin: 5rem auto;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 2rem;
border-radius: 1rem;
box-shadow: 0 0 1rem rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
#main {
width: 50%;
margin: auto;
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
font-size: 3rem;
margin-bottom: 2rem;
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #4b0bff, #68b2ff);
-webkit-background-clip: text;
background-clip: text;
color: transparent;
}
h3 {
font-weight: normal;
}
button {
padding: 0.5rem 0.75rem;
border: none;
background-color: #007bff;
color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 0.5rem;
transition: 0.3s;
margin-left: 0.25rem;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
input[type="number"] {
padding: 0.5rem;
font-size: 1rem;
border: none;
background-color: #e3e3e3;
border-radius: 0.5rem;
}
@media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
body {
color-scheme: dark;
color: white;
background: #2b0057;
}
h1 {
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #4facfe, #00f2fe);
}
.container {
background: #16022c;
}
input[type="number"] {
background-color: #33194d;
}
}
You should see this if you're in dark mode:

And this if you're in light mode:
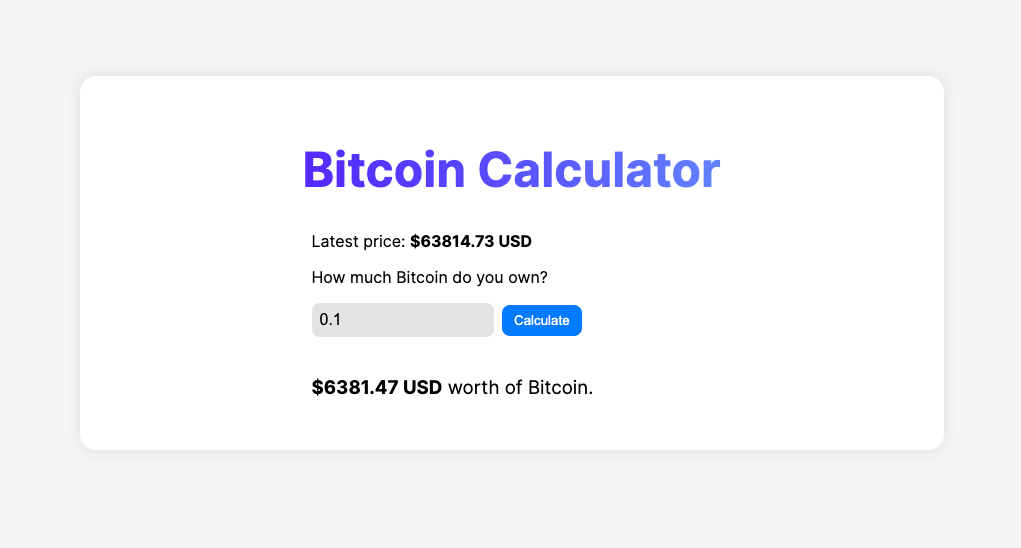
And that's everything!
You can see it on GitHub here:
Here's the live preview:
Conclusion
Feel free to check out my LinkedIn (eszhd) or GitHub (eesazahed).
If you'd like to reach out, my email address is eszhd1@gmail.com